Imagine you’re the CISO of a rapidly growing tech company. Your infrastructure is expanding daily, and with each new line of code, the potential attack surface grows. How do you ensure your systems remain secure?
In the debate of bug bounty vs penetration testing, two popular approaches have emerged: Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS) and Bug Bounty Programs. But are these methods complementary, or do they compete for the same space in your cyber security strategy?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of Bug Bounty vs Penetration Testing, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and how they fit into the broader landscape of continuous security testing.
Whether you’re a seasoned security professional or new to the field, this article will provide valuable insights to help you make informed decisions about your organization’s vulnerability management approach.
The Evolution of Security Testing
Before we compare PTaaS and Bug Bounty Programs, let’s briefly explore how we got here:
Traditional Penetration Testing
Historically, organizations relied on scheduled penetration tests – typically annual or quarterly engagements where security experts would attempt to breach systems and identify vulnerabilities. While effective, this approach had limitations:
- Point-in-time nature: Only provided a snapshot of security at a specific moment
- Limited scope: Often focused on predefined systems or attack vectors
- Resource-intensive: Required significant time and budget to organize and execute
The Rise of Bug Bounty Programs
In the early 2000s, companies like Netscape and Mozilla pioneered the concept of bug bounty programs. These initiatives invited ethical hackers worldwide to find and report vulnerabilities in exchange for rewards. Bug bounties offered:
- Continuous testing: Vulnerabilities could be reported anytime
- Diverse perspectives: A global pool of researchers with varied expertise
- Pay-for-results model: Organizations only paid for confirmed vulnerabilities
The Emergence of PTaaS
As cloud technologies matured, a new model emerged: Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS). This approach aimed to combine the depth of traditional pentesting with the continuity of bug bounties, leveraging automation and on-demand expertise. Now, let’s delve into each approach in detail.
Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS)
Definition and Key Features
PTaaS is a cloud-based model that provides continuous or on-demand penetration testing services.
Key features include:
- Automated and manual testing components
- Real-time reporting and dashboards
- Integration with existing security tools and workflows
- Access to a team of security experts
Benefits of PTaaS:
- Continuous Coverage: Unlike traditional pentests, PTaaS offers ongoing testing, allowing for quicker identification of new vulnerabilities.
- Scalability: Easily adapt to changing infrastructure and application landscapes.
- Consistency: Standardized methodologies ensure thorough and repeatable testing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Often more budget-friendly than maintaining an in-house red team.
- Compliance Support: Many PTaaS offerings include compliance-specific testing and reporting.
Limitations of PTaaS
- Potential for Over-Reliance on Automation: While automation is powerful, it may miss nuanced vulnerabilities that require human insight.
- Limited Creativity: Testers may follow predefined methodologies, potentially missing unconventional attack vectors.
- Fixed Skill Set: The expertise is limited to the PTaaS provider’s team.
Bug Bounty Programs
Definition and Key Features
Bug bounty programs are crowdsourced security initiatives where organizations reward independent researchers for discovering and reporting vulnerabilities. Key features include:
- Open invitation to a global community of ethical hackers
- Defined scope and rules of engagement
- Tiered reward structure based on vulnerability severity
- Managed platforms for submission, triage, and communication
Benefits of Bug Bounty Programs
- Diverse Expertise: Access to a wide range of skills and perspectives from researchers worldwide.
- Pay-for-Results: Organizations only pay for valid, unique vulnerabilities.
- Potential for Novel Discoveries: Creative approaches may uncover unexpected vulnerabilities.
- Competitive Element: Researchers are incentivized to find high-impact issues quickly.
- Brand Building: Can demonstrate a commitment to security and transparency.
Limitations of Bug Bounty Programs
- Unpredictable Costs: High-severity findings can lead to significant, unplanned payouts.
- Noise and False Positives: Requires resources to triage and verify submissions.
- Scope Management: Challenging to control exactly what gets tested and when.
- Potential for Reputational Risk: Public programs may expose vulnerabilities before they’re fixed.
Bug Bounty vs Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS)
Now that we’ve explored each approach in detail, let’s compare them across key factors:
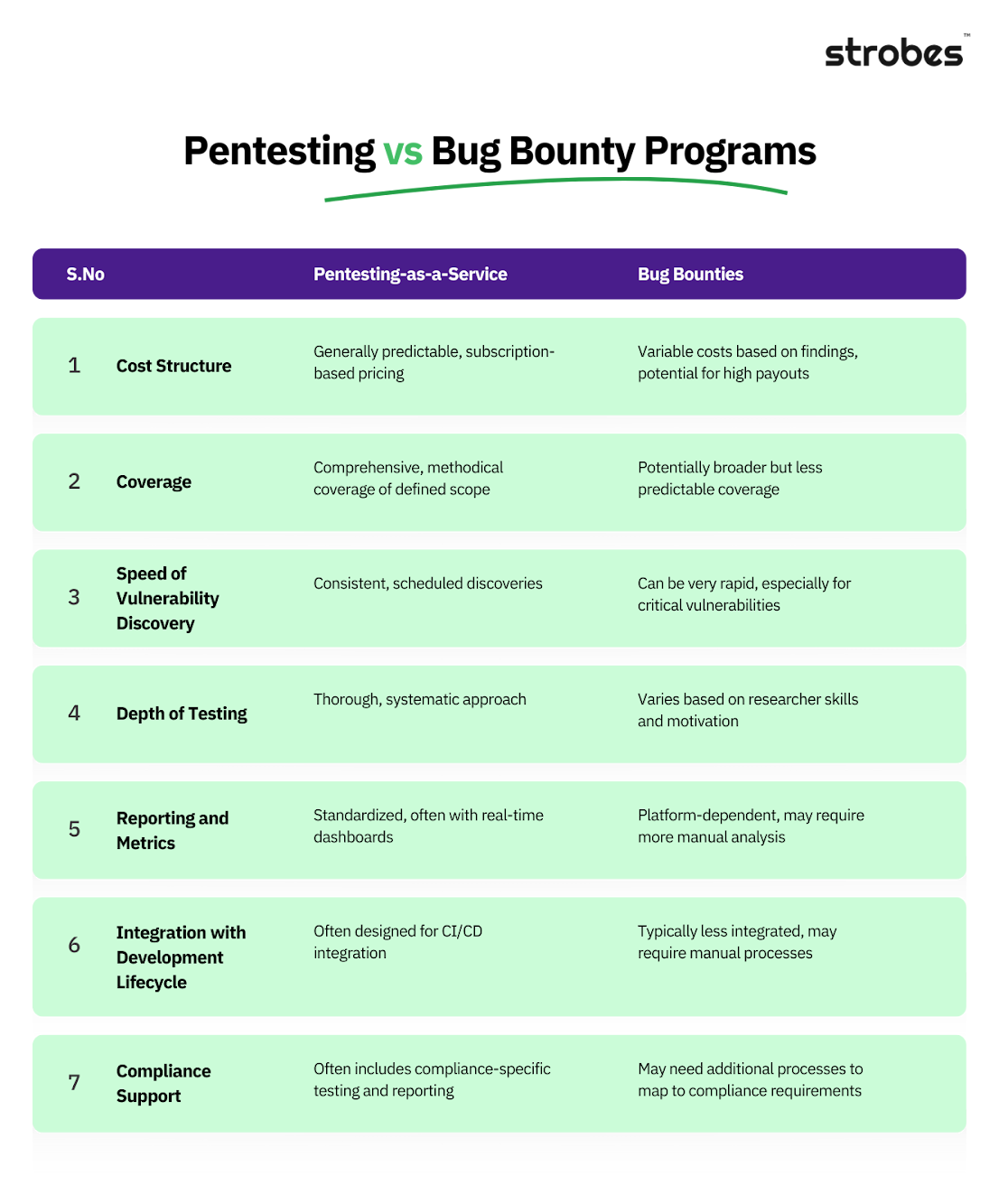
Real-World Examples
Penetration Testing (PTaaS) Success
A financial services company implemented a Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS) model to enhance their security posture. Previously, the company conducted annual penetration tests, but they were concerned about the lack of visibility and testing coverage between these sporadic assessments. By adopting PTaaS, they were able to run continuous, targeted testing on their critical assets.
In the first quarter alone, the new model identified 30% more vulnerabilities compared to their last annual test. This proactive approach enabled them to prioritize and address high-risk vulnerabilities sooner, thereby reducing their attack surface and improving overall security hygiene.
Bug Bounty Win
A social media platform, facing growing security concerns, opted to launch a bug bounty program alongside internal security audits. Within the first month, a researcher uncovered a critical data exposure vulnerability that standard penetration tests had missed. This highlighted a key insight in the bug bounty vs penetration testing discussion while traditional tests are structured and periodic, bug bounty programs harness diverse, real-world perspectives continuously.
The discovery not only prevented a potential data breach but also validated the effectiveness of crowdsourced security. As a result, the company expanded its bug bounty program to cover more assets and incentivize deeper vulnerability discovery.
Hybrid Approach
An e-commerce giant found success with a hybrid security testing model. They use PTaaS to continuously assess the security of their core infrastructure, such as payment processing systems and internal databases. This continuous testing provides quick feedback on vulnerabilities, helping the company maintain compliance and a robust security posture.
For their customer-facing applications, like their shopping portal and API gateways, they run a public bug bounty program, encouraging independent researchers to identify edge-case vulnerabilities that may not be covered in automated testing. This combined approach maximizes coverage, accelerates vulnerability discovery, and balances costs between automated and crowdsourced efforts.
Challenges and Considerations
Resource Allocation
Both PTaaS and bug bounty programs require dedicated resources for management and remediation. PTaaS involves ongoing engagements with testing providers, maintaining the environment, and reviewing results.
Similarly, bug bounty programs need continuous oversight to triage incoming reports, validate findings, and determine appropriate rewards. The time and cost involved in both models can strain security and development teams if not properly managed.
Skill Gap
A significant challenge is ensuring that internal teams have the right skills to interpret findings and act on them. PTaaS often produces more frequent and varied results, requiring a deep understanding of penetration testing methodology.
Likewise, bug bounty programs might produce high volumes of submissions, including duplicates or low-quality reports, making it crucial to have skilled personnel for effective triage and remediation. This often necessitates additional training or hiring specialized talent.
Cultural Shift
Moving to a continuous testing model like PTaaS, or opening up the environment to external researchers through bug bounties, often requires a shift in organizational mindset. Companies used to periodic assessments may struggle with the shift to ongoing monitoring and the need for rapid responses.
Additionally, some teams might view external testing with skepticism, leading to resistance that must be addressed through clear communication and internal advocacy for the new approach.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
In the context of bug bounty vs penetration testing, bug bounty programs particularly require a well-defined legal framework to protect both the organization and participating researchers. Unlike traditional penetration testing, which is controlled and contracted, bug bounty initiatives open the door to external contributors making clear rules of engagement, defined scopes, and legal boundaries essential.
Without proper structure, these programs can lead to disputes over intellectual property, unauthorised testing, or data privacy violations. Establishing expectations early ensures legal clarity and program success.
Check out: The Legal and Ethical Considerations of Penetration Testing
Future Outlook
As we look ahead, several trends are likely to shape the evolution of PTaaS and bug bounty programs:
1. Increased AI Integration
AI will play an increasingly pivotal role in both PTaaS and bug bounty programs, enabling smarter and faster detection, classification, and prioritization of vulnerabilities. AI-driven testing can identify patterns, anomalies, and attack vectors that traditional methods might miss, and automate triage, reducing the workload on security teams. This trend will likely reshape how both models operate and streamline the testing lifecycle.
2. Shift-Left Security
Organizations are focusing on integrating security earlier in the development lifecycle, a trend known as “Shift-Left” security. This means that PTaaS and bug bounty models will likely be integrated more closely with CI/CD pipelines and development processes, providing feedback as code is written, tested, and deployed. This shift helps catch vulnerabilities earlier, reducing costs and minimizing the risk of post-deployment exploits.
3. Regulatory Influence
As data privacy and cybersecurity regulations evolve, compliance requirements will increasingly shape security testing strategies. PTaaS, with its continuous monitoring and reporting capabilities, may be favored by organizations needing to meet stringent regulatory standards. At the same time, regulations may impact bug bounty programs by placing limits on what can be tested and how data is handled, pushing companies to refine their frameworks and operational processes.
4. Specialization
As security threats become more complex, the landscape of penetration testing vs bug bounty is also evolving. We may see a shift toward more specialized PTaaS offerings and bug bounty programs tailored to specific industries or technologies.
For instance, dedicated PTaaS for cloud-native environments, IoT devices, or blockchain systems could emerge, focusing on their unique challenges. Likewise, bug bounty programs may adapt to uncover niche vulnerabilities, attracting experts with highly specialized skills to tackle these emerging threats.
Complementary or Competing?
So, is the debate around penetration testing vs bug bounty about complementary strategies or competing approaches? The answer, as with many things in cybersecurity, is nuanced. While they can compete for budget and attention, PTaaS and bug bounty programs often work best in tandem. PTaaS provides the consistent, comprehensive coverage needed for ongoing security assurance, while bug bounty programs offer the potential for unexpected, high-impact discoveries.
The ideal approach for many organizations is a layered strategy:
- Implement PTaaS for continuous, systematic testing of critical assets.
- Use bug bounty programs to supplement with creative, crowdsourced perspectives.
- Integrate both into a broader vulnerability management program that includes internal processes, automated scanning, and periodic deep-dive assessments.
By leveraging the strengths of both PTaaS and bug bounty programs, organizations can create a robust, multi-faceted approach to vulnerability management that adapts to the ever-changing threat landscape.
As you consider your organization’s security testing strategy, ask yourself:
- Are we getting the comprehensive coverage we need?
- Are we leveraging diverse perspectives to uncover potential blind spots?
- How well do our current practices integrate with our development lifecycle?
When evaluating your current vulnerability management strategy, consider the dynamics of bug bounty vs penetration testing. A thorough assessment can reveal how PTaaS and bug bounty programs might complement your existing efforts. Don’t hesitate to start small—many providers offer pilot programs or limited-scope engagements to help assess their fit.
In cyber security, standing still is moving backward. Embrace continuous improvement to stay ahead of evolving threats. Want to see it in action? Book a demo and discover how the right approach can elevate your security game.
Related Reads:
- Why Penetration Testing Is Important: Enhancing Security & Reducing Cyber Risks
- How much does a penetration test cost?
- How Strobes Penetration Testing Supports Compliance Audits and Assessments
- Penetration Testing Explained: Safeguarding your Online Presence
- Decoding the Penetration Testing Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Solution: Pentesting as a Service