The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has implemented a comprehensive Cyber Security Framework tailored for Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) to bolster their defenses against evolving cyber threats. This framework is designed to enhance cyber resilience, protect sensitive information, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. As UCBs increasingly depend on digital technologies, adopting a robust cyber security framework is essential for safeguarding financial data and maintaining operational integrity.
RBI Cyber Security Framework For Urban Cooperative Banks
Get Audit Consultation
Key Components of the Framework
Governance Structure
- Develop and implement a comprehensive policy outlining the bank’s approach to managing cyber risks.
- Establish a dedicated committee to oversee cybersecurity measures and ensure compliance with the framework.
Risk Assessment and Management
- Conduct periodic risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and assess potential impacts.
- Implement an incident response plan to manage and mitigate the effects of cyber incidents
Technology Controls
- Implement strict access control mechanisms to restrict unauthorized access to systems and data.
- Use encryption to protect data both in transit and at rest.
Operational Controls
- Deploy firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to safeguard the network.
- Regularly update software and systems to address vulnerabilities.
Third-Party Risk Management
- Evaluate the security practices of third-party vendors.
- Include cyber security clauses in vendor contracts.
Compliance and Reporting
- Report cyber incidents to the RBI as required.
- Conduct regular audits and reviews of cyber security practices.
Level-Based Cyber Security Standards for UCBs
Given the varied nature of Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs), a universal cyber security framework isn’t feasible. The RBI has introduced a tiered approach, categorizing UCBs into four levels. Banks should perform a self-assessment to identify their level according to the specified criteria.
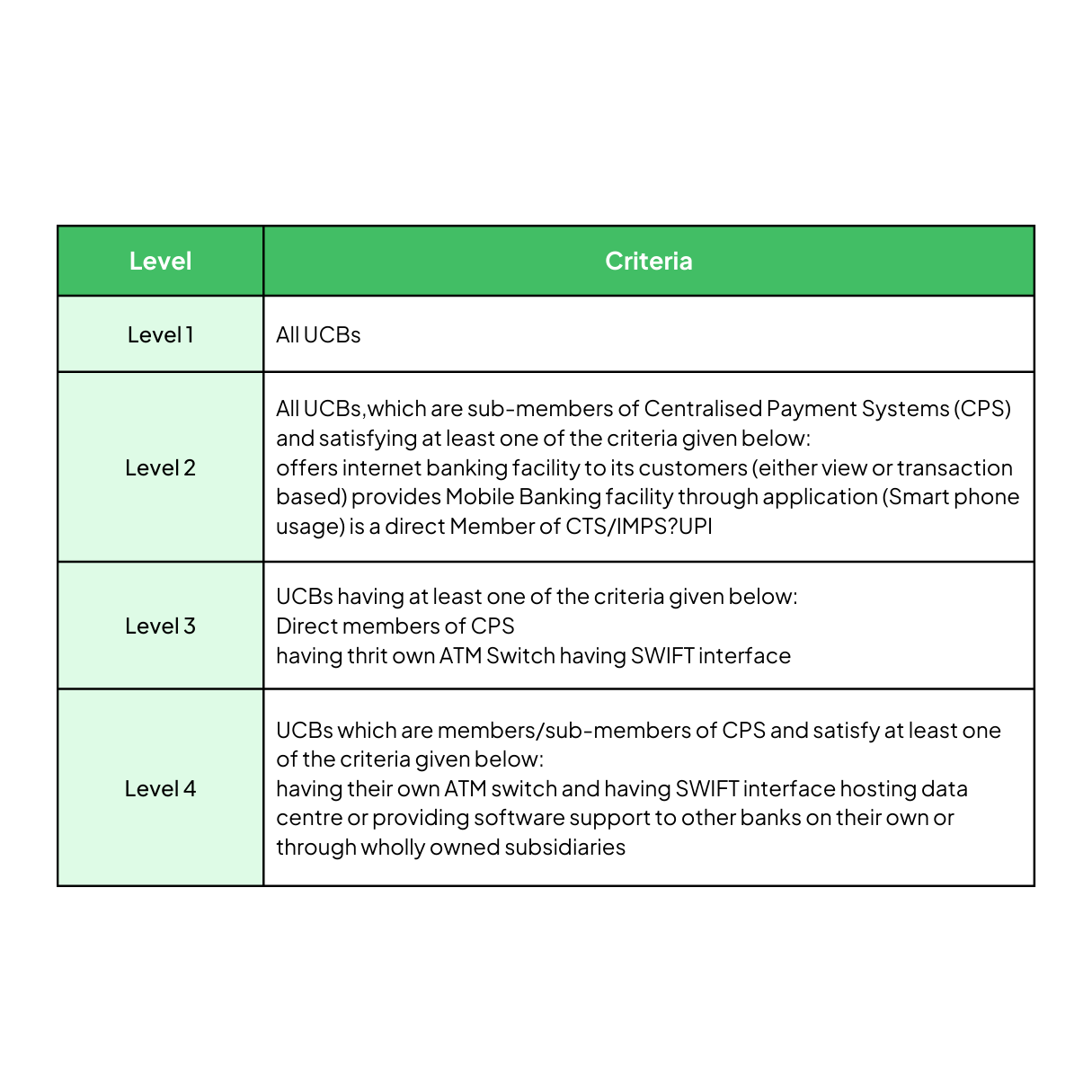
RBI Circulars
Cyber Security Framework in Banks: DBS. CO/CSITE/BC.11/33.01.001/2015-16
This framework outlines the essential cyber security measures for banks, emphasizing a structured approach to managing and mitigating cyber risks. It includes guidelines on policy creation, risk assessment, and incident response tailored to the banking sector’s needs. The framework ensures that banks implement effective security controls to protect their information systems and customer data.
Basic Cyber Security Framework for Primary (Urban) Cooperative Banks (UCBs): DCBS.CO.PCB.Cir.No.1/18.01.000/2018-19
This circular provides a fundamental cyber security framework specifically for Primary Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs), focusing on essential security measures and best practices. It includes guidelines for policy development, risk management, and basic security controls. The framework aims to establish a foundational level of security appropriate for the size and scope of these banks.
Comprehensive Cyber Security Framework for Primary (Urban) Cooperative Banks (UCBs) – A Graded Approach: DoS.CO/CSITE/BC.4083/31.01.052/2019-20
This framework introduces a graded approach to cyber security for Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs), recognizing different levels of risk and security needs. It provides detailed guidelines for implementing advanced security measures based on the bank’s size and complexity. The approach ensures that UCBs apply appropriate controls tailored to their specific cyber risk profile.
Cyber Security Controls for Third Party ATM Switch Application Service Providers: DoS.CO/CSITE/BC.4084/31.01.015/2019-20
This framework specifies the cyber security controls required for third-party ATM switch application service providers. It outlines standards for protecting the integrity and security of ATM switch applications, ensuring that service providers implement robust measures to safeguard against cyber threats. The framework is designed to protect both the service provider and the banks using their systems.
Audit Methodology
Ready to elevate your security journey?
Frequently asked questions
How does the framework ensure the security of the centralized payment systems (CPS)?
The framework includes specific guidelines from RBI circulars that outline access criteria and security protocols for centralized payment systems. It emphasizes the need for stringent controls over data access, transaction processing, and system integration to safeguard CPS operations.
What role does the Cyber Security Operations Center (C-SOC) play?
The C-SOC is responsible for proactive monitoring, threat detection, and incident response. It uses advanced data analytics tools and detection techniques to identify and mitigate potential cyber threats in real-time, ensuring ongoing protection of the bank’s infrastructure.
How often should Urban Cooperative Banks perform risk assessments?
How should Urban Cooperative Banks handle and report cyber incidents?
Banks must establish processes for managing and monitoring cyber security incidents and report significant occurrences to the RBI as required. They should also update incident management policies to facilitate information sharing on forums such as the CISO forum and IB-CART, ensuring transparency and collaboration in addressing cyber threats.
What are the compliance requirements for Urban Cooperative Banks under this framework?
Banks must develop and implement a comprehensive cyber security policy, conduct regular risk assessments, establish a Cyber Security Operations Center (C-SOC), and adhere to reporting requirements for cyber incidents. Compliance also involves ensuring that third-party vendors meet security standards and integrating cyber security into overall business processes.




