March 2025 was a high-alert month for cybersecurity teams.
Critical CVEs surfaced across widely used technologies, some quiet, others loud, but all carrying real risk. These weren’t just routine disclosures. They were vulnerabilities with the potential to disrupt operations, expose data, and create serious security gaps if left unaddressed.
In this blog, we break down the top CVEs & Vulnerabilities of March 2025, what they impact, why they matter, and what your team should be doing about them.
Let’s take a closer look.
1.CVE-2025-24985: Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Fast FAT File System Driver
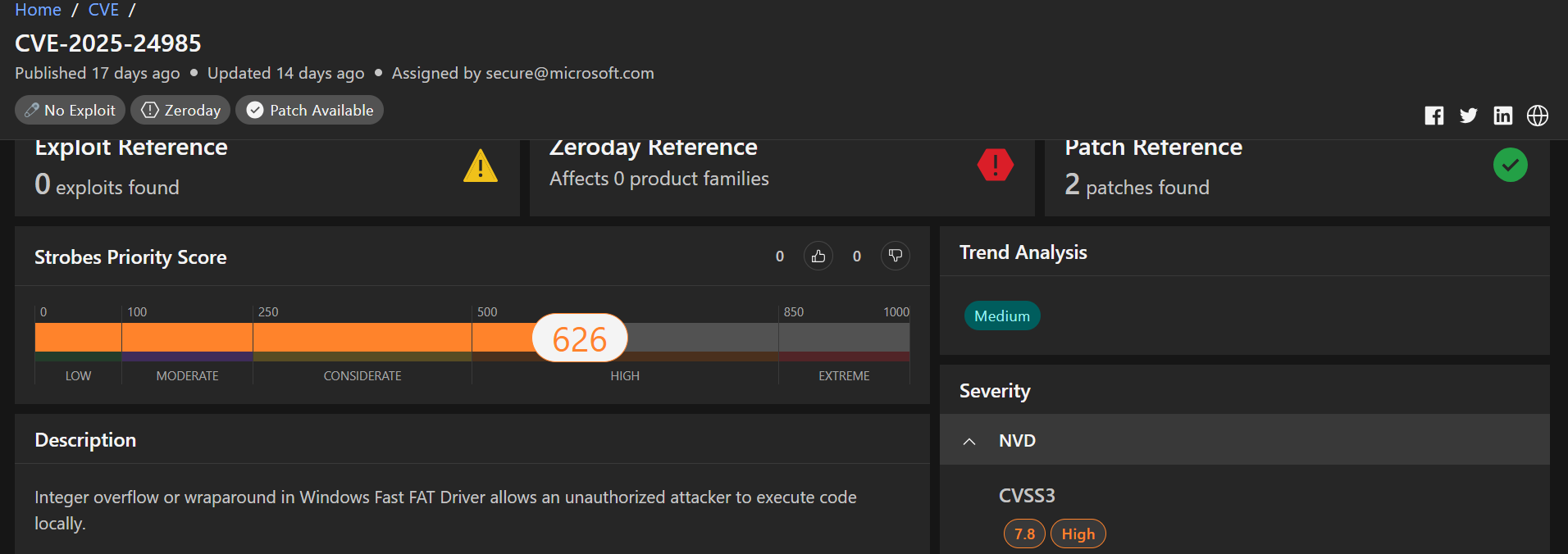
CVE-2025-24985 is a significant security vulnerability affecting the Windows Fast FAT File System Driver, a component responsible for handling the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system in Windows operating systems. This vulnerability enables Remote Code Execution (RCE), allowing an attacker to execute arbitrary code on a target system under specific conditions.
Discovered and patched in March 2025, it was actively exploited as a zero-day prior to the release of Microsoft’s security update, making it a high-priority concern for organizations and individuals using Windows.
Impact
Successful exploitation of CVE-2025-24985 can lead to serious consequences:
- System Compromise: An attacker could gain control over the affected system by executing malicious code, potentially escalating privileges to administrative levels.
- Data Exposure or Loss: Sensitive data stored on the compromised system could be accessed, exfiltrated, or destroyed, depending on the attacker’s intent.
- Malware Deployment: The vulnerability could serve as an entry point for deploying ransomware, spyware, or other malicious payloads.
- Operational Disruption: Critical systems relying on the affected Windows environment could experience downtime or degraded performance, impacting business operations.
Details of the Vulnerability
Severity: Important
CVSS Score: 7.8 (CVSSv3: AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H)
- Attack Vector: Local
- Attack Complexity: Low
- Privileges Required: None
- User Interaction: Required
- Scope: Unchanged
- Confidentiality/Integrity/Availability Impact: High
Affected Products: Microsoft Windows (all supported versions using the Fast FAT File System Driver, including Windows 10, 11, and Server editions)
Vulnerability Type: Remote Code Execution (RCE)
Exploitability: Local attack requiring user interaction, typically via mounting a specially crafted virtual hard disk (VHD). Actively exploited in the wild as a zero-day prior to patching.
The vulnerability stems from improper handling of certain operations within the Fast FAT driver, allowing an attacker to craft a malicious VHD that, when mounted by a user, triggers a buffer overflow or similar memory corruption issue. This leads to the execution of attacker-controlled code. While it requires user interaction (e.g., convincing a user to open the VHD), the low complexity and lack of privilege requirements make it a potent threat, especially in phishing or social engineering campaigns.
Mitigation
Microsoft addressed CVE-2025-24985 in its March 2025 Patch Tuesday update. To protect systems, the following steps are recommended:
Apply Updates Immediately:
Install the latest security update from Microsoft (March 2025 Patch Tuesday release) for all affected Windows versions. This patch corrects the flaw in the Fast FAT File System Driver and is the most effective defense.
Additional Best Practices:
- User Education: Train users to avoid mounting unknown or untrusted VHDs, especially from email attachments or unverified sources, as this is a common exploitation vector.
- Restrict VHD Mounting: Use Group Policy or endpoint security solutions to limit who can mount VHDs on critical systems.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Deploy EDR tools to monitor for suspicious activity, such as unexpected code execution or VHD-related anomalies.
- Least Privilege: Ensure processes and users operate with minimal permissions to reduce the impact of successful exploitation.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems to limit lateral movement if a breach occurs.
Prompt patching is essential, given the confirmed exploitation in the wild. Organizations should also verify patch deployment across all systems using vulnerability management tools.
Why Top Ranked?
CVE-2025-24985 earned its position as the top-ranked CVE for March 2025 due to several critical factors:
- Zero-Day Exploitation: It was actively exploited in the wild before Microsoft released a patch, indicating real-world attacker interest and capability.
- Widespread Impact: The Fast FAT File System Driver is a core component of Windows, affecting a vast number of systems across consumer, enterprise, and server environments.
- Historical Significance: This marks the first exploited vulnerability in the Windows Fast FAT driver since 2022, highlighting a rare and noteworthy attack surface.
- Ease of Exploitation: Despite requiring user interaction, the low attack complexity and lack of privilege requirements make it accessible to attackers, especially when paired with social engineering tactics like phishing.
Its combination of active exploitation, broad applicability, and potential for significant damage distinguishes it as a top priority for immediate remediation in March 2025.
Source
2.CVE-2025-24993: Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows NTFS
CVE-2025-24993 is a significant security vulnerability affecting the Windows New Technology File System (NTFS), a core component of Microsoft Windows operating systems. This vulnerability allows for Remote Code Execution (RCE), enabling an attacker to execute arbitrary code on a vulnerable system.
Discovered and patched in Microsoft’s March 2025 Patch Tuesday release, it was actively exploited in the wild as a zero-day prior to the patch, making it a high-priority concern for organizations and individuals relying on Windows environments.
Impact
Successful exploitation of CVE-2025-24993 can lead to severe consequences:
- Full System Compromise: An attacker could gain complete control over the affected Windows system, executing malicious code with system-level privileges.
- Data Breach: Sensitive data stored on the NTFS file system could be accessed, exfiltrated, or altered, compromising confidentiality and integrity.
- Service Disruption: Critical system processes or applications relying on NTFS could be disrupted, causing downtime or operational failures.
- Lateral Movement: Once exploited, attackers could leverage the compromised system to move laterally within a network, targeting additional systems or resources.
Details of the Vulnerability
Severity: Important (Microsoft rating)
CVSS Score: 7.8 (High severity; based on exploitability and impact metrics)
Affected Products: Microsoft Windows operating systems (all supported versions using NTFS, including Windows 10, 11, and Server editions)
Vulnerability Type: Remote Code Execution (RCE) via heap-based buffer overflow
Exploitability:
- Remote: Yes, but requires user interaction (e.g., mounting a crafted virtual hard disk).
- Attack Complexity: Moderate (requires crafting a malicious VHD and social engineering to trick a user into mounting it).
- Privileges Required: None (no prior authentication needed, though local access to mount the VHD is necessary).
- User Interaction: Required (user must mount the malicious VHD).
The vulnerability stems from a heap-based buffer overflow in the NTFS driver when processing specially crafted virtual hard disk (VHD) files. An attacker can exploit this by enticing a user to mount a malicious VHD, triggering the overflow and allowing arbitrary code execution. Its status as a zero-day, exploited before a patch was available, underscores its real-world threat.
Mitigation
Microsoft addressed CVE-2025-24993 in the March 2025 Patch Tuesday update. The primary mitigation steps include:
- Apply Updates Immediately: Install the latest Windows security updates released in March 2025 to patch this vulnerability. This is the most effective and critical step to eliminate the risk.
Additional Best Practices:
- User Education: Train users to avoid mounting unknown or untrusted VHD files, especially from external sources like email attachments or unverified downloads.
- Restrict VHD Mounting: Use Group Policy or system configurations to limit which users can mount VHDs, reducing the attack surface.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Deploy EDR tools to monitor for suspicious file-mounting activities or exploitation attempts.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems to limit the spread of an attack if exploitation occurs.
- File Integrity Monitoring: Implement tools to detect unauthorized changes to file systems that might indicate exploitation.
Prompt patching is essential, as active exploitation has been confirmed in the wild. Organizations should prioritize this update alongside regular security hygiene practices to minimize exposure.
Why Top Ranked?
CVE-2025-24993 ranks among the top CVEs of March 2025 due to its combination of real-world exploitation, significant impact, and widespread applicability. As a zero-day vulnerability actively targeted before the patch, it posed an immediate threat to millions of Windows systems worldwide. Its focus on NTFS, a fundamental component of Windows, means virtually all supported Windows versions were at risk, amplifying its potential for widespread damage.
Source
- Microsoft March 2025 Patch Tuesday Security Update
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
3.CVE-2025-25181: Advantive VeraCore SQL Injection Vulnerability
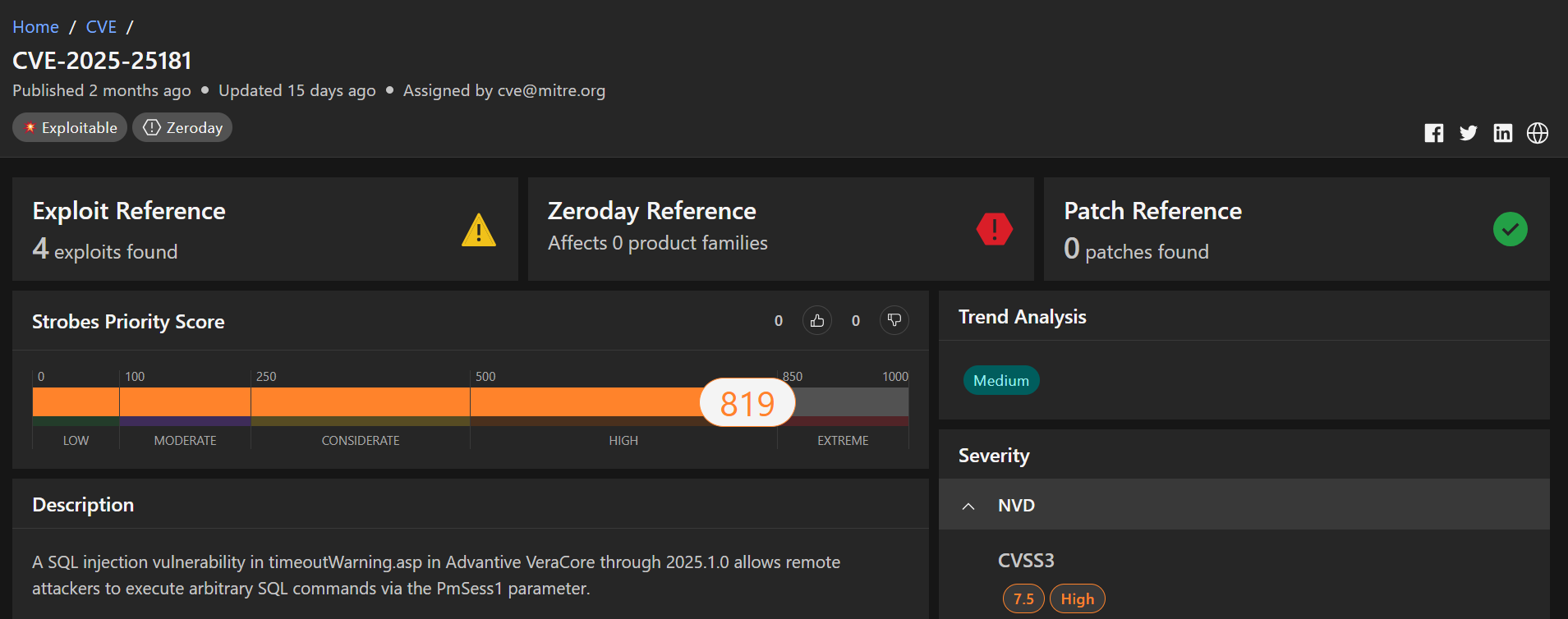
CVE-2025-25181 is a significant security vulnerability affecting Advantive VeraCore, a software solution used for order fulfillment, warehouse management, and e-commerce operations. This vulnerability is classified as a SQL injection flaw, which allows an attacker to manipulate the database queries executed by the application.
By injecting malicious SQL code, an attacker can bypass authentication, extract sensitive data, or even alter the database, posing a serious risk to businesses relying on VeraCore for critical operations.
Impact
Successful exploitation of CVE-2025-25181 can lead to severe consequences for affected organizations:
- Data Breach: Attackers can extract sensitive information such as customer data, order details, or financial records stored in the VeraCore database.
- Unauthorized Access: By bypassing authentication mechanisms, attackers could gain administrative access to the system, compromising its integrity.
- Data Manipulation: Malicious actors could alter or delete critical business data, such as inventory records or transaction logs, leading to operational chaos.
- Business Disruption: Exploitation could disrupt warehouse and e-commerce operations, resulting in downtime, lost revenue, and reputational damage.
- Lateral Movement: Once inside the system, attackers could pivot to other networked systems, amplifying the scope of the attack.
Details of the Vulnerability
- Severity: High (specific CVSS score not yet published in the National Vulnerability Database as of March 28, 2025, but inferred from CISA KEV inclusion).
- CVSS Score: Pending official assignment; likely in the 7.5–8.5 range based on SQL injection norms and active exploitation.
- Affected Products: Advantive VeraCore (specific versions not fully detailed in public sources as of this date; assume all unpatched versions are at risk).
- Vulnerability Type: SQL Injection
- Exploitability: Remote, Moderate attack complexity, No privileges required, No user interaction (based on typical SQL injection characteristics and CISA’s KEV listing, which prioritizes actively exploited flaws).
Mitigation
Advantive has likely released a patch or guidance to address CVE-2025-25181, given its inclusion in the CISA KEV Catalog, which mandates federal agencies to remediate within a set timeframe (typically 2-3 weeks from listing). To protect against this vulnerability, organizations should:
- Apply Updates Immediately: Install the latest security patches or updates provided by Advantive for VeraCore. Check Advantive’s official support channels for the specific patch release tied to CVE-2025-25181.
- Input Validation: Implement strict input validation and parameterized queries in custom VeraCore configurations to prevent SQL injection attempts.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF): Deploy a WAF to filter and block malicious SQL injection payloads targeting the application.
- Database Hardening: Restrict database permissions to limit the damage potential of a successful injection (e.g., use least-privilege accounts for application queries).
- Monitoring and Logging: Enable detailed logging of database queries and monitor for anomalous activity, such as unexpected SELECT, DROP, or UPDATE statements.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate VeraCore servers from other critical systems to contain potential breaches.
- Regular Backups: Maintain up-to-date backups of the VeraCore database to enable rapid recovery in case of data tampering.
Organizations must act swiftly, as CISA’s KEV listing on March 9, 2025, confirms that this vulnerability is being actively exploited, leaving unpatched systems at immediate risk.
Why Top Ranked?
CVE-2025-25181 ranks among the top CVEs of March 2025 due to its inclusion in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, a definitive indicator of real-world exploitation.
SQL injection vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they target the data layer of applications, which in VeraCore’s case underpins business-critical functions like order processing and inventory management. Its impact on e-commerce and logistics sectors,key drivers of the modern economy, elevates its significance.
Source
Trusted by leading enterprises like, GHX, Zoho, Darwinbox, Tricenties, and SHL
Strobes helped organizations continuously manage threats, reduce vulnerabilities, and stay compliant, powered by AI-driven security expertise.
4.CVE-2025-30066: tj-actions/changed-files GitHub Action Embedded Malicious Code Vulnerability
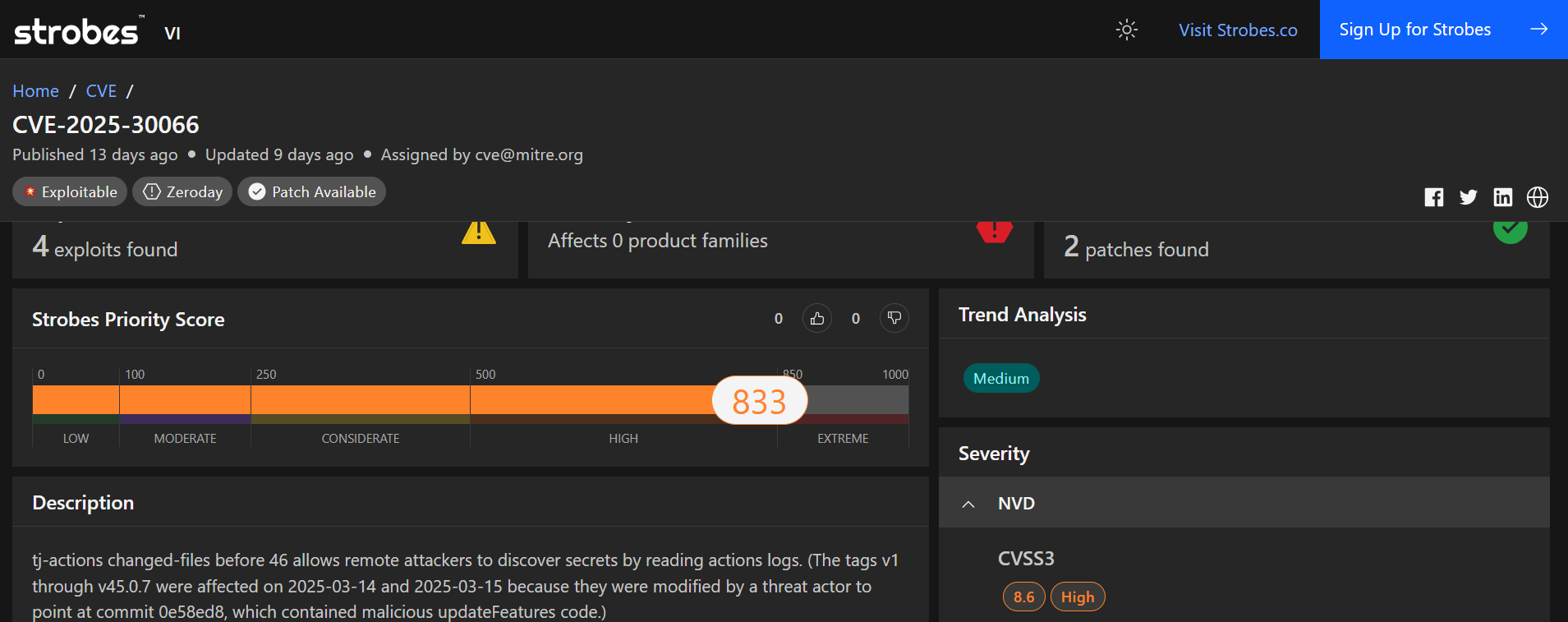
CVE-2025-30066 is a severe security vulnerability identified in the tj-actions/changed-files GitHub Action, a widely used tool in GitHub workflows for identifying changed files in repositories. This vulnerability stems from embedded malicious code within the action, which can lead to the exposure of sensitive secrets and credentials, posing significant risks to organizations relying on GitHub for DevOps and software development pipelines.
Impact
Successful exploitation of CVE-2025-30066 can result in serious consequences:
- Credential Exposure: Secrets such as AWS keys, GitHub tokens, and other sensitive credentials logged in GitHub Actions workflows can be exfiltrated by attackers, compromising cloud infrastructure and repository access.
- Supply Chain Attack: Compromised workflows can be used to inject malicious code into downstream software builds, affecting end users and customers.
- Unauthorized Access: Exposed credentials could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to repositories, cloud services, or other integrated systems.
- Operational Disruption: Breaches resulting from this vulnerability could disrupt CI/CD pipelines, delaying development cycles and deployments.
Details of the Vulnerability
- Severity: High (actively exploited, added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog).
- CVSS Score: Not explicitly assigned in available data as of March 28, 2025, but inferred as high (likely 8.0–9.0) due to its inclusion in CISA’s KEV Catalog and ease of exploitation.
- Affected Products: GitHub repositories using the tj-actions/changed-files GitHub Action (specific versions not detailed in early reports but assumed to be widely deployed ones prior to mitigation).
- Vulnerability Type: Embedded Malicious Code / Supply Chain Vulnerability.
- Exploitability: Remote, Low attack complexity, No privileges required, No user interaction. The vulnerability is triggered simply by running a workflow that includes the affected action, making it highly exploitable in automated environments.
Mitigation
The primary mitigation steps for CVE-2025-30066 include immediate action to secure affected workflows:
Update or Remove the Action: Replace or update the tj-actions/changed-files action to a verified, non-malicious version as recommended by the maintainers or GitHub. Check the official repository for patched releases post-March 2025.
Review Workflow Logs: Audit GitHub Actions logs for any workflows using the affected action to identify potential secret exposure. Revoke and rotate any compromised credentials (e.g., AWS keys, GitHub tokens).
Implement Secret Management: Use GitHub’s encrypted secrets feature properly and avoid logging sensitive data in workflow outputs.
Additional Best Practices:
- Dependency Scanning: Regularly scan GitHub Actions dependencies for known vulnerabilities using tools like Dependabot or third-party security scanners.
- Least Privilege: Limit the permissions of GitHub Actions tokens (e.g., use repository-specific tokens with minimal scope).
- Monitoring: Set up alerts for unusual workflow activity or unauthorized access attempts in GitHub and integrated services.
- Pipeline Isolation: Run workflows in isolated environments to prevent lateral movement if compromised.
Why Top Ranked?
CVE-2025-30066 ranks among the top CVEs of March 2025 due to its significant real-world impact and active exploitation:
- Active Exploitation: Its inclusion in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog near March 27, 2025, confirms that attackers are targeting this flaw, elevating its urgency.
- Supply Chain Implications: As a GitHub Action vulnerability, it threatens the integrity of software supply chains, a growing concern in cybersecurity, especially for open-source and enterprise projects.
- Widespread Use: The tj-actions/changed-files action is popular in GitHub workflows, amplifying the potential attack surface across thousands of repositories.
- Ease of Exploitation: The lack of required user interaction or privileges, combined with the automated nature of CI/CD pipelines, makes this a low-effort, high-reward target for attackers.
Source
5.CVE-2025-22224: Critical VMware ESXi and Workstation TOCTOU Race Condition Vulnerability
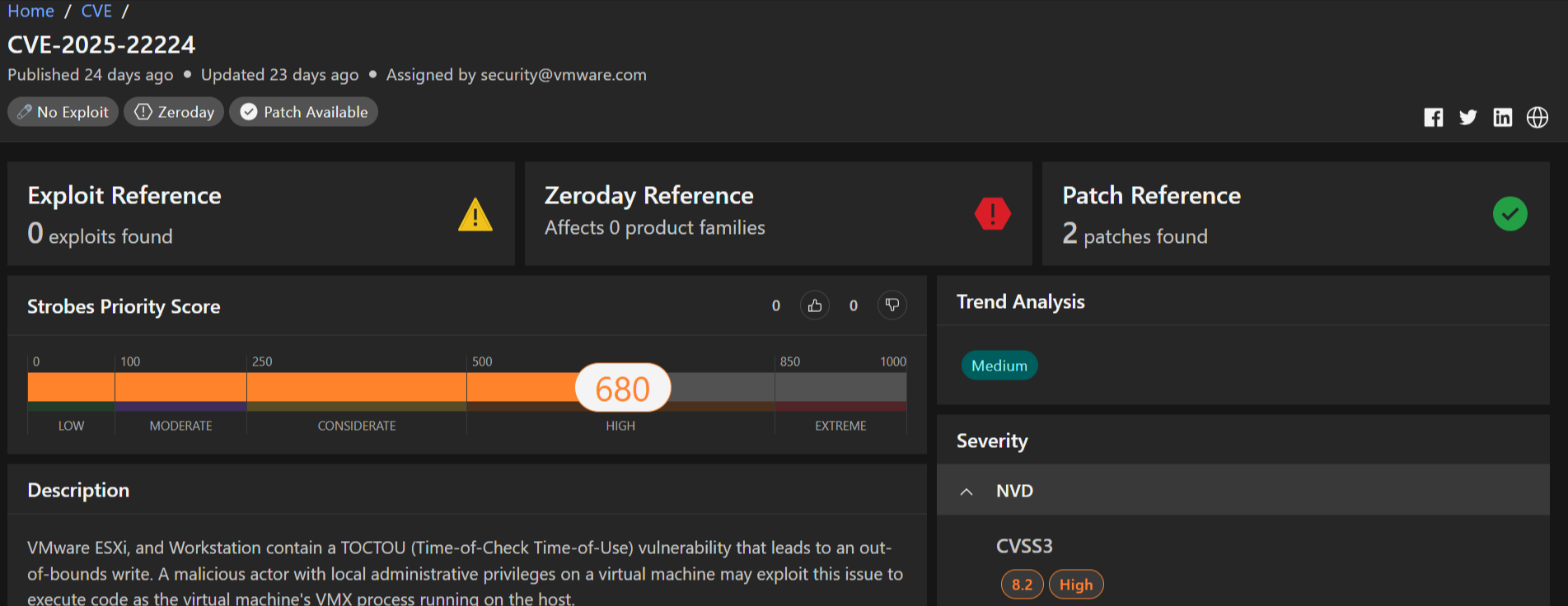
CVE-2025-22224 is a critical security vulnerability affecting VMware ESXi and VMware Workstation, key components of VMware’s virtualization ecosystem. VMware ESXi is a type-1 hypervisor used to deploy and manage virtual machines (VMs) on physical servers, while VMware Workstation is a type-2 hypervisor that enables users to run multiple operating systems on a single desktop or laptop.
This vulnerability is a Time-of-Check Time-of-Use (TOCTOU) race condition that leads to an out-of-bounds write, allowing a malicious actor with local administrative privileges on a virtual machine to execute code as the virtual machine’s VMX process on the host.
The VMX process is responsible for managing the virtual machine’s interaction with the host system, making this a severe flaw that can result in a virtual machine escape, compromising the hypervisor itself.
Impact
Successful exploitation of CVE-2025-22224 can lead to significant and far-reaching consequences:
- Hypervisor Compromise: An attacker can escape the virtual machine sandbox and gain control over the ESXi hypervisor or Workstation host, potentially affecting all VMs running on the system.
- Data Breach: Sensitive data across all virtual machines on the compromised host could be accessed, extracted, or altered, including confidential business data, credentials, or intellectual property.
- Service Disruption: Critical virtualized workloads could be halted or manipulated, leading to downtime, operational inefficiencies, or financial losses for organizations relying on VMware infrastructure.
- Lateral Movement: Once the hypervisor is compromised, attackers could pivot to other systems within the network, expanding the scope of the attack to other hosts, VMs, or connected infrastructure.
Details of the Vulnerability
Severity: Critical
CVSS Score: 9.3
Affected Products: VMware ESXi (versions 7.0–8.0, 6.7), VMware Workstation (version 17.x), and related products like VMware vSphere, Cloud Foundation, and Telco Cloud Platform.
Vulnerability Type: Time-of-Check Time-of-Use (TOCTOU) Race Condition leading to Out-of-Bounds Write
Exploitability: Local, Moderate attack complexity, Administrative privileges required on the VM, No user interaction
Mitigation
Broadcom, VMware’s parent company, addressed CVE-2025-22224 in its security advisory VMSA-2025-0004, released on March 4, 2025, alongside patches for affected products. The primary mitigation steps include:
Apply Updates Immediately: Install the latest security patches provided by Broadcom for VMware ESXi, Workstation, and related products. Fixed versions are detailed in the advisory’s Response Matrix (e.g., ESXi 8.0 Update 3a, Workstation 17.5.2). This is the most effective way to eliminate the vulnerability.
Additional Security Best Practices:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Restrict administrative access to VMs to only trusted users and processes, minimizing the attack surface.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate VMware hosts and VMs from untrusted networks to limit lateral movement in case of a breach.
- Monitoring and Logging: Enable robust logging and monitoring of VM and hypervisor activity to detect suspicious behavior, such as unexpected privilege escalation attempts.
- Access Controls: Enforce strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), for administrative access to virtualization management interfaces.
Why Top Ranked?
CVE-2025-22224 is ranked among the top CVEs for March 2025 due to its critical severity, active exploitation in the wild, and the widespread use of VMware products in enterprise environments. As a zero-day vulnerability, it was exploited before patches were available, increasing its immediate threat level.
The ability to achieve a VM escape and compromise the hypervisor, a foundational layer of virtualization infrastructure, makes it particularly dangerous, especially for organizations hosting sensitive or critical workloads.
Source
Final Thoughts
March 2025 didn’t just drop CVEs, it dropped warnings. Loud ones.
Flaws buried in everyday tools. Exploits hiding in plain sight. And attackers who were quick to move.If that doesn’t make you pause, it should.
The top CVEs of March 2025 weren’t background noise, they were red flags. Miss them, and you’re playing catch-up. Catch them early, and you’re in control.
Want the full picture? Explore Strobes’ Vulnerability Intelligence platform for deeper insights.
Related Reads: