Cyber threats don’t hit pause, and CVEs in January 2025 were no exception. From security flaws in popular software to exploits that kept security teams on high alert, the year started with plenty to unpack. If you’re in charge of protecting your organization or staying informed, knowing which vulnerabilities made waves is essential. Let’s break down the most impactful CVEs of January 2025 and why they matter.
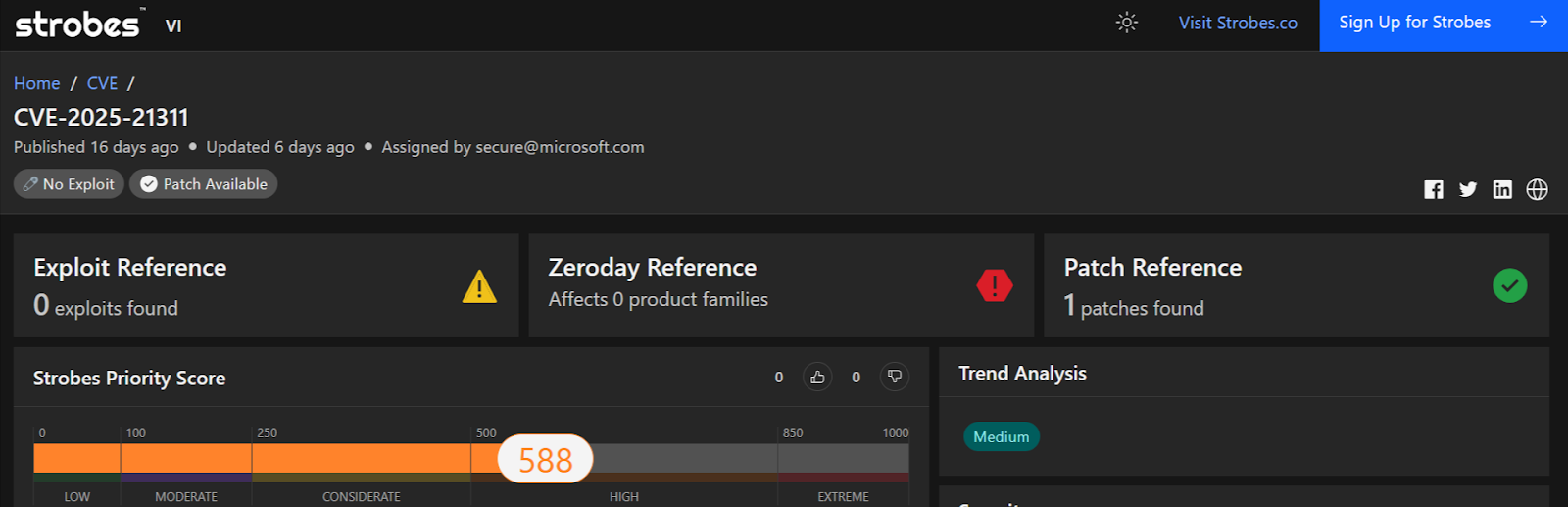
1. CVE-2025-21311: Windows NTLMv1 Authentication Bypass
Impact:
This critical Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerability or CVE-2025-21311 allows attackers to bypass NTLMv1 authentication and gain SYSTEM-level privileges on compromised Windows systems. Exploitation enables lateral movement across networks, credential theft, and persistence in enterprise environments.
Technical Details:
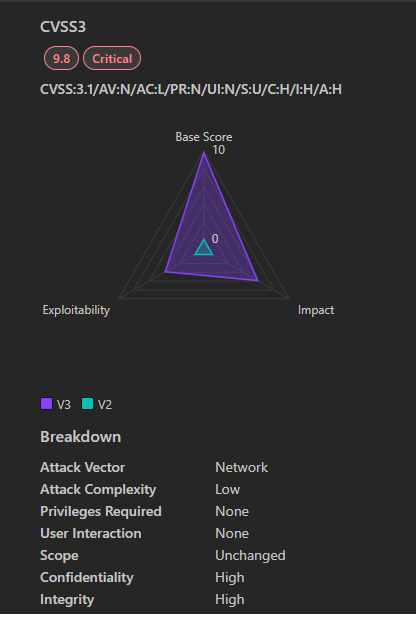
- Severity: Critical (CVSS 9.8)
- CVSS Breakdown:
- Attack Vector: Network (remotely exploitable).
- Complexity: Low (no advanced skills required).
- Privileges: None needed (pre-authentication).
- User Interaction: Not required.
- Affected Products:
- Windows Server 2012–2022, Windows 10/11, and legacy systems with NTLMv1 enabled.
- Vulnerability Type:
Flawed cryptographic hashing in NTLMv1’s challenge-response mechanism. Attackers intercept or forge session keys to impersonate legitimate users. - Exploitability:
Exploited via tools like Responder or Impacket to relay authentication requests. Requires SMB or HTTP traffic with NTLMv1 enabled.
Mitigation:
- Immediate Action:
- Apply Microsoft’s emergency patch KB5034443.
- Disable NTLMv1 via Group Policy: Set LmCompatibilityLevel=5 to enforce NTLMv2.
- Long-Term Hardening:
- Migrate to Kerberos for domain authentication.
- Deploy SMB Signing and monitor for NTLM traffic using tools like Microsoft Defender for Identity.
- Detection:
- Alert on event IDs 4624 (failed logins) and 4648 (explicit credential use) in Windows logs.
- Immediate Action:
Source:
2. CVE-2025-24085: Apple Core Media Framework Zero-Day
Impact:
Actively exploited in targeted attacks, this zero-day CVE-2025-24085 allows privilege escalation and full device control via maliciously crafted media files (e.g., videos, images). Successful exploitation grants kernel-level access, enabling data exfiltration or spyware installation.
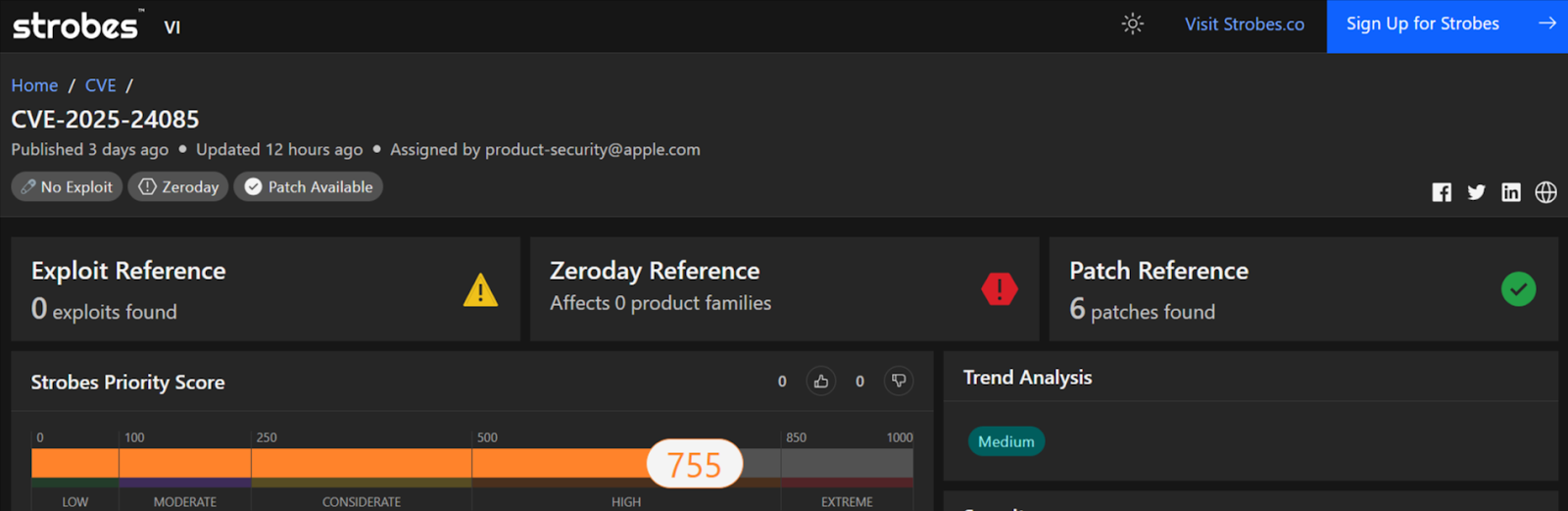
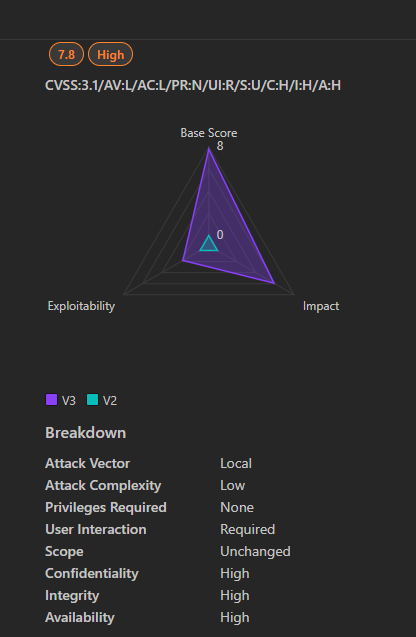
Technical Details:
- Severity: Critical (Apple’s internal classification).
- CVSS Estimate: 9.6 (based on analogous CVEs like CVE-2021-30883).
- Affected Products:
- iOS <17.2, macOS <14.3, VisionOS <1.1, and Apple TV (tvOS <17.2).
- Vulnerability Type:
Use-after-free in the Core Media Framework’s H.264/H.265 video parser. Attackers craft media files with malformed headers to corrupt memory regions. - Exploitability:
- Delivered via malicious apps, phishing links, or AirDrop.
- Exploit chains with CVE-2025-24086 (WebKit flaw) observed in spyware campaigns.
Mitigation:
- Patching:
- Update to iOS 17.2, macOS 14.3, or later.
- Workarounds:
- Disable “Install Unknown Apps” and enforce Lockdown Mode for high-risk users.
- Use MDM solutions to block unapproved app installations.
- Detection:
- Monitor for abnormal process creation (e.g., mediaserverd spawning shells).
- Patching:
Source:
3. CVE-2025-21297: Microsoft Word RTF Remote Code Execution
Impact:
Attackers exploit this CVE-2025-21297 by sending malicious RTF files via email or compromised websites. Successful exploitation grants user-level code execution, which can lead to ransomware deployment or credential harvesting.
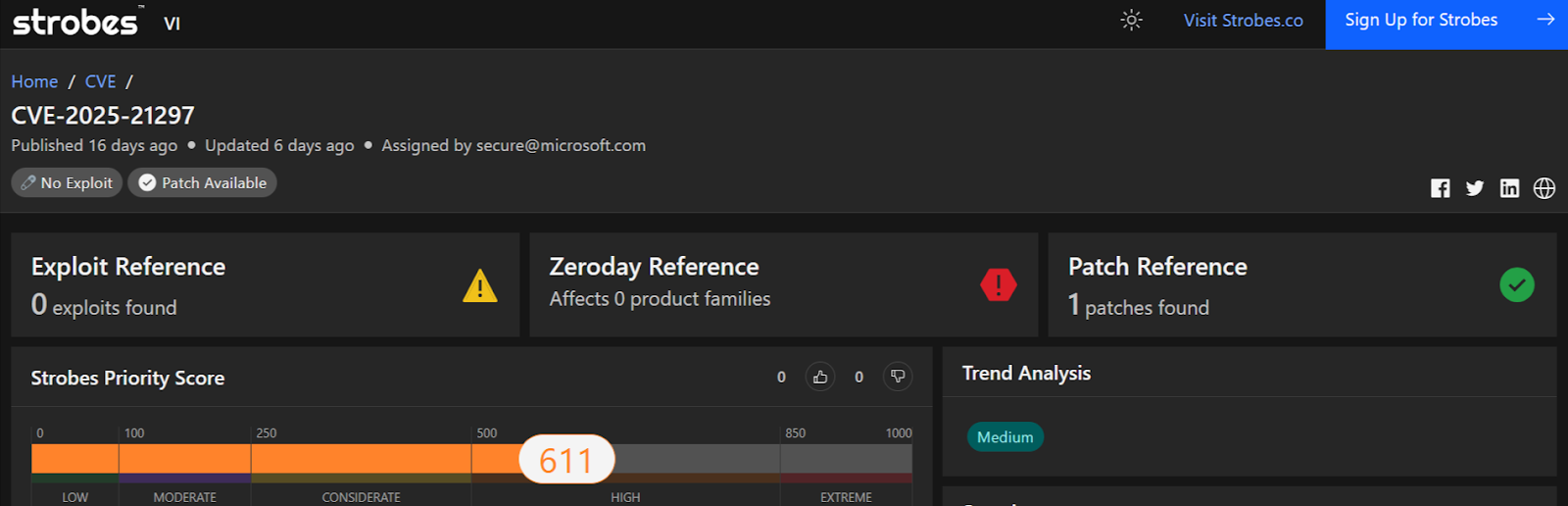
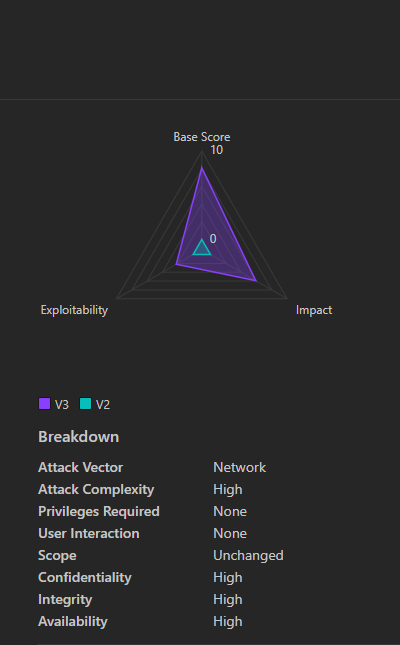
Technical Details:
- Severity: High (CVSS 8.8)
- CVSS Breakdown:
- Attack Vector: Local (user interaction required).
- Impact: High (confidentiality, integrity, and availability loss).
- Affected Products:
- Microsoft Word 2016–2021, Microsoft 365 Apps.
- Vulnerability Type:
Heap buffer overflow in the wwlib.dll library during font parsing. Malicious fonts trigger memory corruption. - Exploitability:
- Phishing campaigns using decoy documents (e.g., “Invoice_2025.rtf”).
- Exploit kits like Magnitude observed distributing payloads.
Mitigation:
- Patching:
- Deploy KB5034447 via Microsoft Update.
- Proactive Defense:
- Block RTF files at email gateways using regex patterns (e.g., \.rtf$).
- Enable Office Protected View and disable ActiveX controls.
- User Training:
- Simulate phishing attacks to educate users on suspicious attachments.
- Patching:
Source:
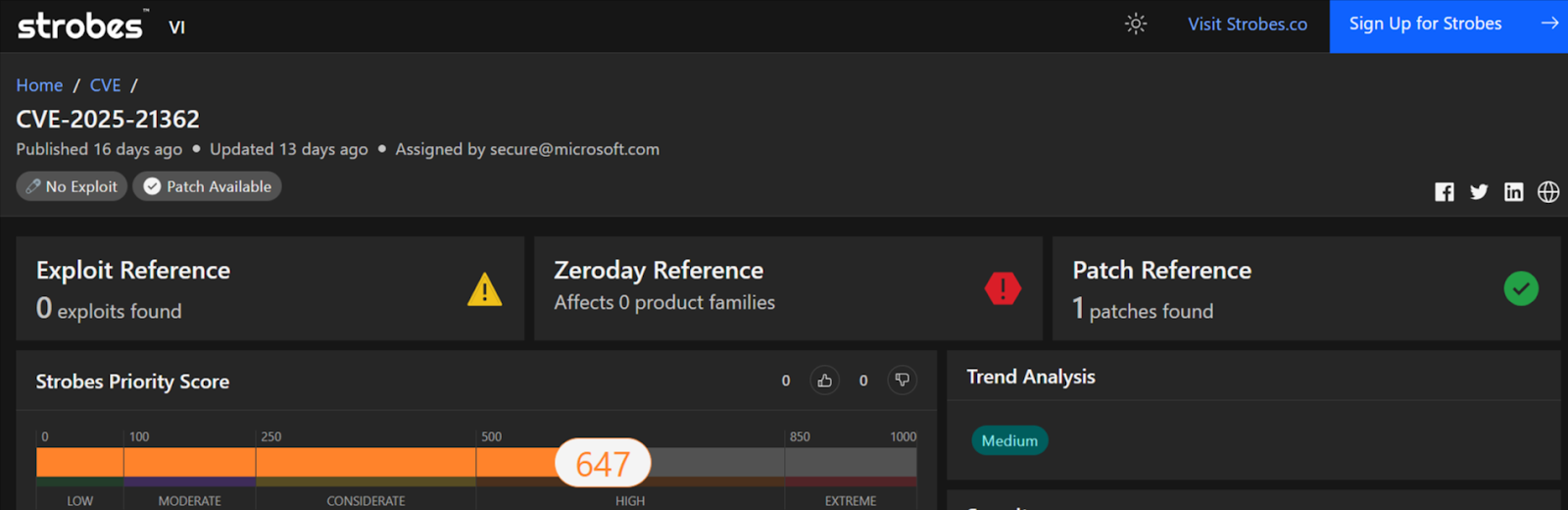
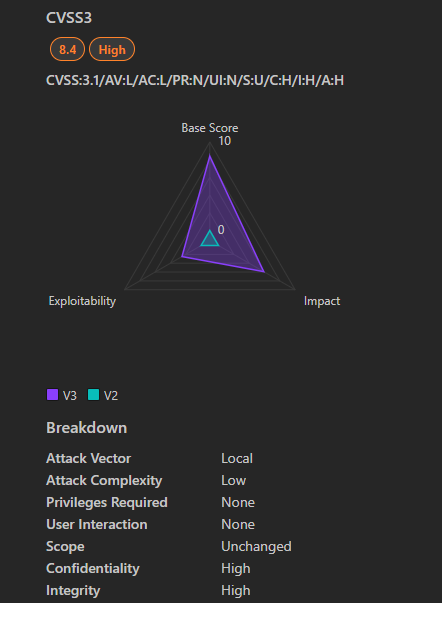
4. CVE-2025-21362: Linux Kernel eBPF Privilege Escalation
Impact:
Local attackers exploit CVE-2025-21362 a flaw in the eBPF verifier, to execute arbitrary code with root privileges, bypassing kernel protections like SELinux or AppArmor.
Technical Details:
- Severity: Critical (CVSS 9.0)
- CVSS Breakdown:
- Attack Vector: Local (physical or shell access required).
- Complexity: Medium (requires crafting eBPF bytecode).
- Affected Products:
- Linux kernels 5.15–6.6 (Ubuntu 22.04+, RHEL 9+, Debian 12).
- Vulnerability Type:
Type confusion in the eBPF verifier’s JIT compiler. Attackers craft eBPF programs that misrepresent pointer types to corrupt kernel memory. - Exploitability:
- Exploit tools like DirtyBPF automate privilege escalation.
- Often chained with initial access vulnerabilities (e.g., CVE-2025-21363: SSH brute-force).
Mitigation:
- Patching:
- Upgrade to kernel 6.6.1+ or apply vendor backports (e.g., Ubuntu linux-image-5.15.0-101).
- Hardening:
- Disable unprivileged eBPF:
- bash
- Copy
- sysctl -w kernel.unprivileged_bpf_disabled=1
- Restrict eBPF with seccomp or LSM policies.
- Detection:
- Audit dmesg logs for eBPF verifier warnings.
- Patching:
Source:
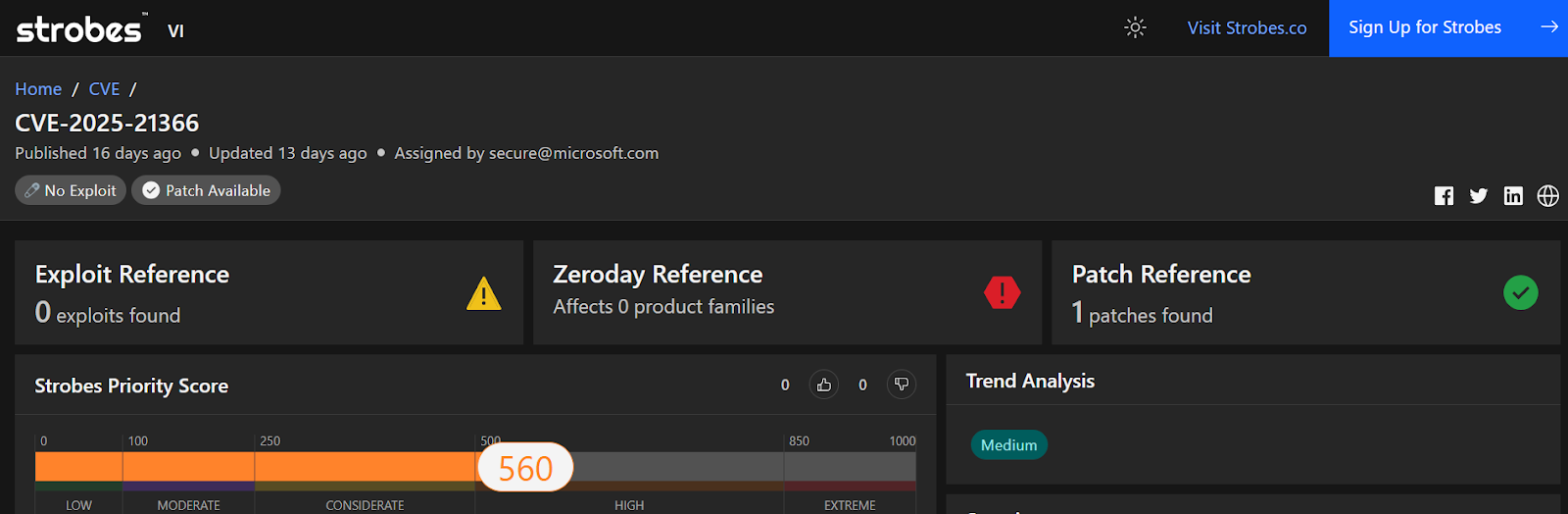
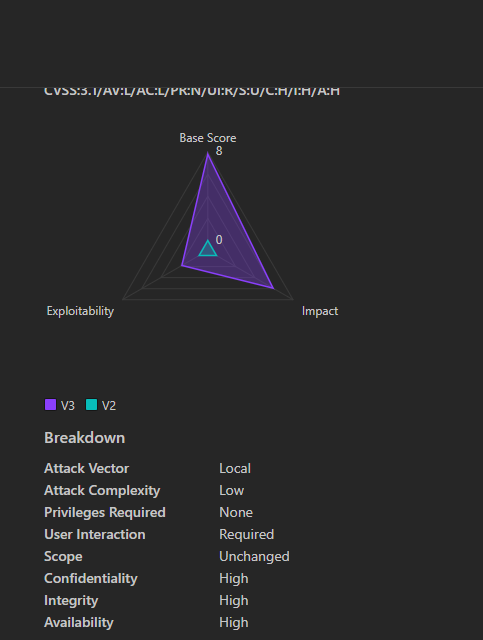
5. CVE-2025-21366: SAP NetWeaver Directory Traversal
Impact:
Authenticated attackers exploit this CVE-2025-21366 to traverse directories, access sensitive files (e.g., passwd, configuration files), or execute arbitrary code on SAP Java Application Servers.
Technical Details:
- Severity: High (CVSS 8.1)
- CVSS Breakdown:
- Attack Vector: Network (HTTP/S requests).
- Privileges: Low (valid user account required).
- Affected Products:
- SAP NetWeaver AS Java 7.30–7.50 (ABAP systems unaffected).
- Vulnerability Type:
Path traversal in the web.xml servlet mapping. Attackers append ../ sequences to URLs (e.g., /sap/public/..%5c../etc/passwd). - Exploitability:
- Exploited via tools like SAP Exploitation Framework or manual curl requests.
Mitigation:
- Patching:
- Apply SAP Note 3333333 to sanitize URL inputs.
- Configuration Hardening:
- Restrict filesystem permissions using chroot jails.
- Deploy SAP Web Dispatcher to filter malicious requests.
- Monitoring:
- Log and alert on abnormal HTTP requests (e.g., GET /sap/public/..%5c..).
- Patching:
Source:
January 2025’s top CVEs remind us that cyber threats never take a break. From zero-days in Apple’s ecosystem to critical flaws in Windows protocols, these vulnerabilities highlight the urgent need for proactive defense.By adopting a risk-based approach and acting swiftly, organizations can cut exposure and keep attackers at bay.For a deeper dive into these CVEs and actionable strategies to tackle them, explore Strobes’ Vulnerability Intelligence platform.