A single incident can halt operations, expose regulated data, and drain both budgets and trust. The purpose of this guide is simple. Help you run a rigorous ransomware readiness assessment that builds real resilience, proves financial value, and satisfies auditors.
This guide is written for readers who want clear steps, measurable checkpoints, and a practical way to align with well-known guidance such as the CISA StopRansomware Guidance and NIST’s Ransomware Profile. These resources outline preparation, prevention, response, and recovery practices that you can adopt and test as part of your assessment. (CISA, NIST Publications)
What is a Ransomware Readiness Assessment
A ransomware readiness assessment is a structured review of people, processes, and technology focused on how well your organization can prevent, detect, respond to, and recover from a ransomware event. It goes deeper than a routine security audit or a once-a-year tabletop.
It validates backup recovery in real environments, verifies that high-risk access is controlled, checks that prioritized weaknesses are fixed and retested, and confirms that your internal and external communications will work under pressure. NIST’s ransomware profile maps these outcomes to the Cybersecurity Framework functions, which you can use as your organizing backbone.
Key outcomes
- An inventory of critical business services and data flows that matter most during an incident.
- A plain-English gap list with business impact, cost to fix, and a remediation owner for each item.
- Evidence that backups and restores meet your time and point objectives.
- A short set of metrics that leadership can track every quarter.
Why you cannot ignore ransomware readiness
- Direct financial loss and downtime. Even a brief outage can ripple across sales, support, and supply chains. CISA’s guide highlights how common initial access paths, such as compromised credentials and remote access, lead to operational disruption and data extortion.
- Regulatory and legal exposure. Sector rules and security laws now expect prompt incident reporting, strong access control, tested backups, and clear documentation. HIPAA guidance, for example, stresses security risk analysis, workforce training, and breach notification practice for health entities. (HHS.gov)
- Board accountability. Boards ask simple questions. What are our top business services at risk? How fast can we recover? What controls failed in last quarter’s exercises? A readiness assessment gives you grounded answers.
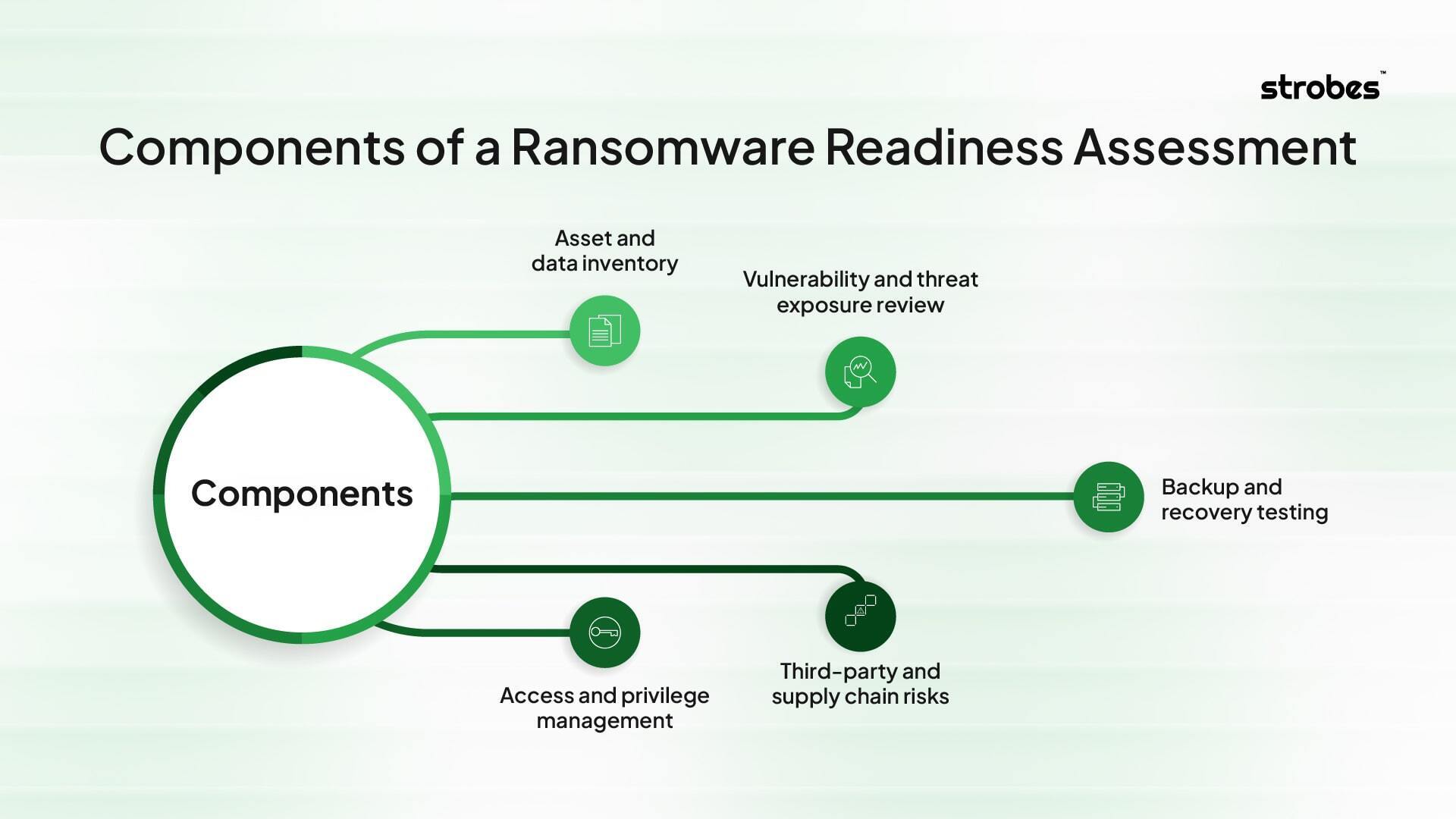
Key components of a ransomware readiness assessment
1 Asset and data inventory
Start where impact lives. Identify the business services that generate revenue or keep operations running. Map the applications, databases, SaaS tenants, identities, and third-party connections behind those services. Tag sensitive data sets and recovery tiers. Your output is a living register that tells responders and recovery teams what to protect first and what to restore first.
Tips
- Include “hidden” estates such as lab environments, unmanaged cloud accounts, and contractor-controlled systems.4
- Tie each asset to a service owner and a restore priority.
- Validate discovery through automated scanners plus stakeholder interviews to catch blind spots.
2 Vulnerability and threat exposure review
The goal is not to fix every weakness. It is to remove the paths attackers use the most. Use risk-based vulnerability management and continuous threat exposure management to focus on issues with known exploits, internet exposure, or privilege escalation potential. Track time to remediate for high-impact items and confirm with retesting. CISA’s guidance groups prevention practices by initial access paths, which is a strong way to organize your backlog.
Tips
- Connect scanner outputs to exploit intelligence so “exploited in the wild” items float to the top.
- Treat identity weaknesses as high priority. Over-privileged service accounts and stale access often translate into rapid spread.
3 Backup and recovery testing
Backups exist to be restored. Run frequent, scripted, and timed restore drills for your top services. Validate both Recovery Time Objective and Recovery Point Objective against business expectations. NIST SP 800-34’s contingency planning guidance is helpful when setting recovery priorities and documenting alternate procedures. (NIST Computer Security Resource Center)
Tips
- Keep at least one copy that is immutable and isolated. Test restores from that copy on a regular schedule.
- Measure restore success rate, average restore time per system, and data currency at restore.
4 Access and privilege management
Limit the blast radius. Enforce strong multi-factor authentication for all privileged accounts and remote access, segment administrative duties, and use just-in-time elevation where possible. HHS’s ransomware guidance underscores the role of access control and training in breach prevention for health entities, and the same logic applies across industries.
Tips
- Review emergency access procedures and audit trails.
- Rotate keys and tokens on a fixed cadence and track completion.
- Block legacy protocols and unused remote access methods.
5 Incident response and retesting
A plan only works if people can execute it. Use the NIST incident response lifecycle to structure playbooks and exercises. Preparation, detection and analysis, containment and eradication, and post-incident improvement should be clear and tested.
The 2025 NIST update aligns response activities with CSF 2.0, which is useful when you brief leadership. After each fix, retest controls to prove they work as expected.
Tips
- Maintain pre-approved communications for customers, regulators, law enforcement, and partners.
- Define decision rights for paying ransoms, engaging negotiators, and notifying insurers before an incident occurs.
- Run short, frequent scenario drills. Alternate business-hours and off-hours runs.
6 Third-party and supply chain risks
Your resilience depends on your suppliers. Review contracts for incident reporting timelines, data handling duties, backup expectations, and cooperation during investigations. Prioritize vendors with network access, sensitive data, or operational control. Track each vendor’s security attestations, pentest frequency, and recovery commitments.
Tips
- Require rapid notification of compromise that could affect you.
- Validate that vendors can provide forensic data on request.
- Map critical dependencies and build alternate options where feasible.
Measuring Resilience: Important Metrics to Consider
Metrics should be short, repeatable, and tied to real outcomes.
- Mean Time to Detect and Mean Time to Respond. Aim for steady reduction by removing alert noise, tuning detections to ransomware behavior, and rehearsing handoffs.
- RTO and RPO by service tier. Track both targets and actuals from restore drills. NIST contingency planning guidance is a reliable reference when setting and testing these numbers.
- Backup restore success rate. Percentage of restores completed within target time with correct data currency.
- Exploit-driven remediation rate. Portion of exploitable, internet-exposed, or privilege-escalation weaknesses fixed within agreed timelines.
- Access hygiene score. A simple composite across MFA coverage for admins and remote users, dormant account removal, and high-risk protocol blocks.
- Incident exercise score. Pass rate for tabletop, technical drill, and full restore exercises.
- Supplier readiness index. Percentage of top suppliers with current assessment, tested recovery commitments, and contractual reporting timelines that meet your obligations.
Demonstrating ROI from ransomware readiness
Security programs get funded when leaders can see cost reductions and risk reductions in business terms. Use these angles.
- Downtime avoided: Model the cost per hour of a top business service and compare restore drill times to past incidents or to industry incident durations. Even a modest reduction in recovery time has an outsized effect on loss avoidance.
- Incident scope reduction: Show how identity hardening and segmentation limited lateral movement during red-team or purple-team exercises. Translate “fewer systems affected” into saved rebuild hours and shorter service impact.
- Operational efficiency: Automate the heavy lifting, such as deduplication of scanner findings and ticket creation to the right owner. Measure analyst time saved per month.
- Compliance cost reduction: Map your assessment artifacts to required controls under sector laws and security rules. Reuse evidence for audits.
Add staffing time saved, supplier penalties avoided, and legal costs reduced to get a fuller ROI view.
Compliance and regulatory alignment
Readiness is not only about technology. It is also about meeting reporting timelines and control expectations.
United States
- CISA CIRCIA proposed rule. Covered entities would report substantial cyber incidents within 72 hours and ransom payments within 24 hours. Plan to capture incident artifacts, prepare legal review steps, and be ready to file within the timelines once final. (Federal Register, The Conference Board)
- HIPAA. Health entities should maintain a strong risk analysis, enforce access control, train staff, and follow breach notification steps that account for ransomware. OCR materials reinforce these expectations.
European Union
- NIS2. Entities must have risk analysis, incident response, and timely incident reporting. Several summaries note notification within 24 hours for significant incidents, so readiness plans should include rapid detection, triage, and authority communication steps. (Navex)
- DORA for financial services. In force since January 17, 2025. It sets strict expectations for ICT risk management, incident reporting, resilience testing, and third-party oversight. Map your assessment to these pillars and ensure incident reporting playbooks meet the rule. (eiopa.europa.eu)
- Cyber Resilience Act. Entered into force on December 10, 2024. It phases in obligations for product security and incident reporting, with most obligations applying from December 2027. If you build or ship software or hardware into the EU, align product teams and incident reporting lines now. (Digital Strategy)
India
- CERT-In Directions. Report specified cyber incidents within six hours and keep ICT logs for 180 days within the jurisdiction. Your readiness assessment should confirm logging meets scope, retention, and accessibility requirements, and that reporting templates and contacts are current. (Cert-In, National Pension System Trust)
Practical checklist for compliance mapping
- Assign an owner for each applicable law or rule.
- Prepare authority-specific notification templates.
- Keep evidence packs for exercises, training, and restores.
- Track supplier contractual obligations and reporting windows that match your own.
Common gaps found during assessments
- Backups exist but restores are not tested: Organizations often capture data well, but only a restoration proves value. Establish recurring drills for top services, measure results, and fix bottlenecks.
- Identity weaknesses: Over-privileged accounts, unused service principals, and weak MFA coverage open the door to rapid spread. Treat identity scope as part of your top risk backlog.
- No single owner for recovery: Security owns detection, IT owns platforms, and application teams own data and logic. Without an incident manager and clear decision rights, time is lost.
- Unclear supplier expectations: Contracts lack timelines, forensic cooperation, or recovery commitments. Vendor due diligence must include incident playbooks and testing outcomes.
- Tool silos: Findings stay in scanners or spreadsheets. Without workflow integration to ITSM and developer tools, remediation stalls.
- Communication not rehearsed: Customer messages, regulator notifications, and partner outreach are drafted during the crisis. Keep approved templates ready and update them after each exercise.
Build a continuous ransomware readiness program
A one-off review helps, but attackers iterate. Treat readiness as a continuous program.
Cadence
- Quarterly risk review for top services.
- Monthly exploit-driven remediation sprints.
- Scheduled restore drills with published targets and results.
- Rolling supplier assessments for critical vendors.
CTEM alignment: Continuous Threat Exposure Management provides a simple way to keep the program live. Identify exposures, assess impact, prioritize, validate with testing, and improve controls. Tie each cycle to metrics such as remediation time and restore performance.
Red-teaming and purple-teaming: Use realistic scenarios. For example, start with exposed credentials, move to privilege escalation, then attempt data staging. Measure how fast detections fire, how quickly isolation occurs, and how clean the restore is.
Post-exercise improvements: Close the loop with specific tasks, clear owners, and deadlines. Retest fixed items to confirm that results hold.
How Strobes Security supports ransomware readiness assessment
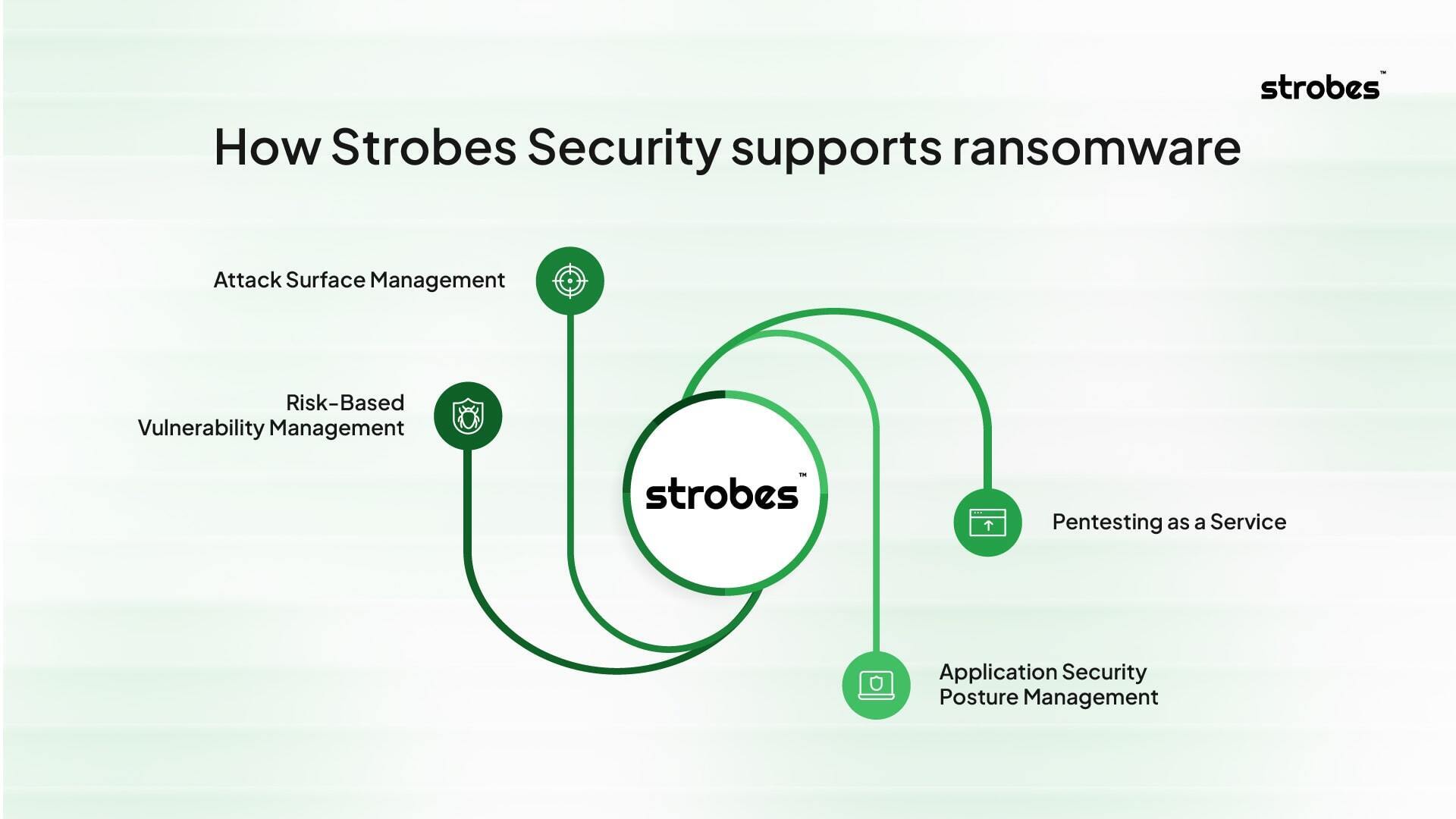
Strobes brings asset discovery, risk-based prioritization, continuous validation, and integrated reporting together so your team can run a readiness program without busywork.
Attack Surface Management
- Unified asset inventory across on-prem, cloud, and SaaS estates.
- Shadow IT detection through continuous discovery.
- Context with ownership, business service mapping, and exposure details.
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
- Exploit-aware prioritization. Strobes weighs exploit availability, internet exposure, data sensitivity, and business context so high-impact items rise to the top.
- Automation. Findings are deduplicated and routed to the right owners in Jira, ServiceNow, Azure DevOps, or email with SLAs.
- Retesting workflow. Once a fix is reported, Strobes schedules and tracks verification, so you move from “closed” to “proven.”
Pentesting as a Service
- Scenario-driven tests that reflect common ransomware entry paths such as exposed remote access and privilege escalation.
- Rapid reporting with clear exploit chains, business impact, and recommended fixes.
- Continuous validation. Re-runs confirm that controls hold during new releases or infrastructure changes.
CTEM program support
- Exposure pipeline. Identify, assess, prioritize, and validate on a continuous loop.
- Metrics and dashboards. Show MTTD and MTTR trends, restore drill outcomes, exploit-driven remediation rates, and supplier readiness at a glance.
- Evidence packs. Exportable summaries for audits and board reports, mapped to frameworks and regulations referenced in this guide, including CISA guidance, NIST, HIPAA, NIS2, DORA, and CERT-In.
Conclusion
Ransomware readiness is a business program. When you know your most important services, cut off common paths of entry, test recovery to measured targets, and rehearse your response, you reduce impact and satisfy regulatory expectations. Using a clear metric set, you can show how readiness work translates into fewer outages, quicker restores, and lower compliance risk.
Book a free demo with Strobes today and see how our platform helps you streamline ransomware readiness assessments, strengthen resilience, and stay audit-ready.