Automated Vulnerability Management: What It Is & Why You Need It
Likhil ChekuriAugust 22, 2025
Organizations nowadays are struggling with a growing IT environment, cloud-based workloads, APIs, IoT devices, and containerized applications are just a few of the ingredients thrown into the mix. With every new asset comes the potential to grow the attack surface area, along with the possibility of introducing vulnerabilities. In 2024 alone, more than 29,000 new CVEs were documented by the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), and that number increases year over year.
Legacy approaches to vulnerability tracking, like spreadsheets, manual scanning, and isolated remediation workflows, are unable to handle this volume. Security teams are typically swamped by the sheer volume of findings and cannot prioritize what's most important.
This is where automated vulnerability management comes into play. Through the replacement of manual effort with automation, organizations can continually discover, scan, prioritize, and fix vulnerabilities at scale, with remediation efforts aligned to actual business risks.
In this blog, we’ll break down what automated vulnerability management is, how it works, why manual methods fall short, and the benefits and best practices of adopting this approach.
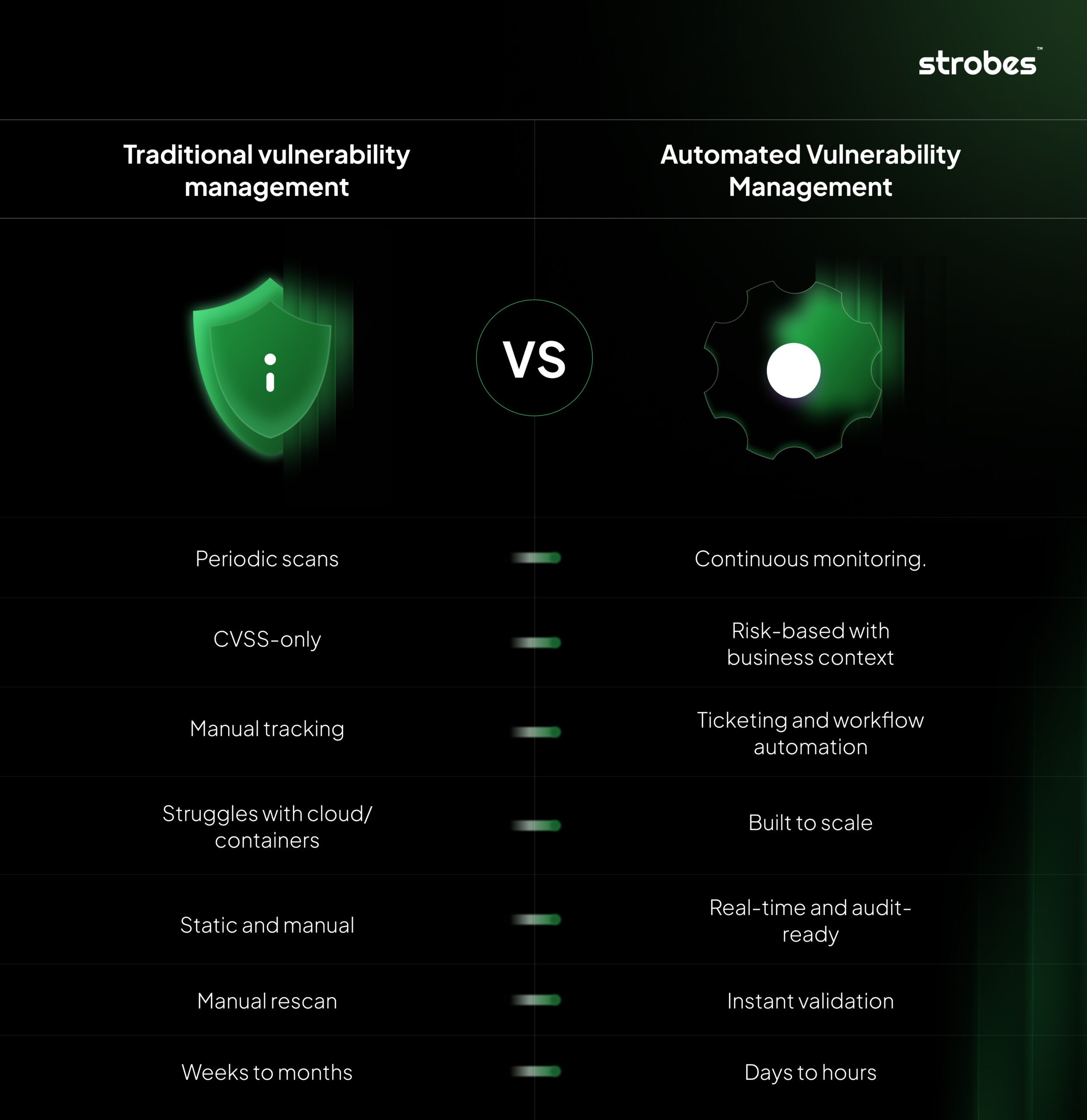 In the image below, we provided a detailed comparison between traditional vulnerability management and automated vulnerability management. This analysis will clarify the key differences, emphasizing the advantages of automation in enhancing security practices.
In the image below, we provided a detailed comparison between traditional vulnerability management and automated vulnerability management. This analysis will clarify the key differences, emphasizing the advantages of automation in enhancing security practices.
What Is Automated Vulnerability Management?
Automated vulnerability management is all about using automation tools and processes to keep a constant eye on, analyze, prioritize, and fix vulnerabilities within an organization's IT infrastructure. Instead of relying on those occasional manual scans, automation enables ongoing monitoring and immediate responses.Key Features of Automated Vulnerability Management
Automated Asset Discovery:
The foundation of any vulnerability management program is knowing exactly what assets exist in your environment. Manual inventory often misses unmanaged devices, shadow IT, or newly deployed cloud workloads. Automated asset discovery continuously scans networks, cloud accounts, containers, and endpoints to maintain a real-time inventory. This ensures that no device, application, or integration slips under the radar.Continuous Scanning:
Instead of relying on one-off assessments, automated systems perform ongoing scans. They integrate with multiple scanners such as:- SAST (Static Application Security Testing) for analyzing source code.
- DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) for evaluating live applications.
- SCA (Software Composition Analysis) for identifying risks in open-source components.
- Container and Kubernetes Security Scanning for detecting issues within containerized environments.
- Secret Scanning for spotting exposed credentials or API keys in repositories.
Vulnerability Correlation & Deduplication:
When multiple scanners are running, results often overlap. Without correlation, security teams waste hours triaging duplicate findings. Automated correlation consolidates these results into a single, unified view and removes duplicates. This not only cuts down noise but also makes remediation workflows much more efficient.Risk-Based Prioritization:
Not all vulnerabilities require the same urgency. Traditional approaches often rely only on CVSS scores, which don’t provide the full context. Automated prioritization combines:- Exploit intelligence (whether attackers are actively exploiting it).
- Business context (how critical the affected asset is to operations).
- Severity scores (CVSS and beyond).
Workflow Automation:
One of the biggest challenges in vulnerability management is closing the gap between discovery and remediation. Automation solves this by pushing vulnerabilities directly into ITSM and DevOps tools such as Jira, ServiceNow, or GitHub. Tickets are automatically assigned to the right teams, with all necessary context included, eliminating delays caused by manual hand-offs.Compliance Monitoring:
It generates automated reports to help with regulatory compliance and audits for standards like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. By automating these processes, security teams can save time, reduce human error, and ensure that remediation efforts align with the actual risk exposure.How Automated Vulnerability Management Works?
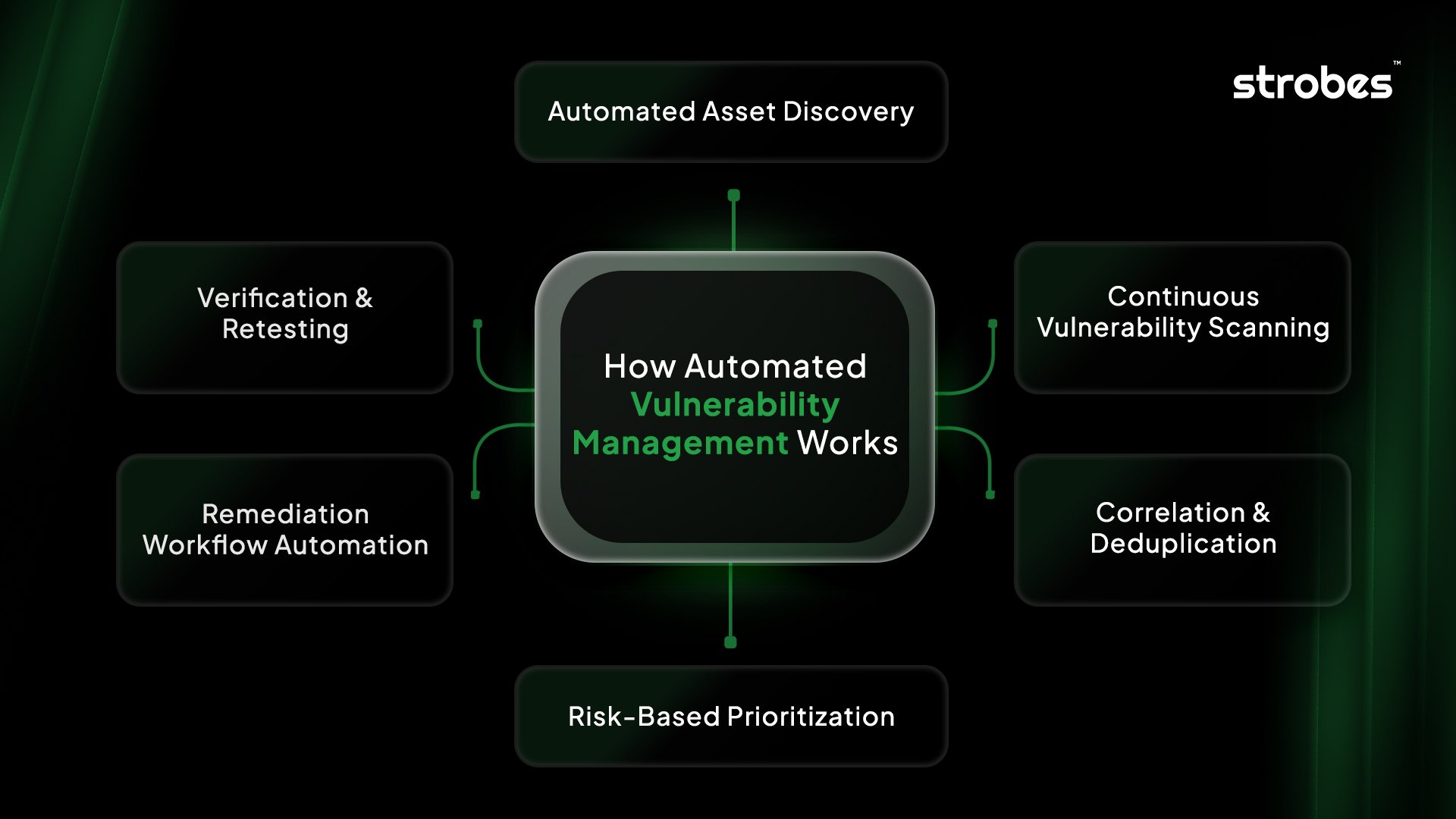
The journey of automated vulnerability management usually unfolds in a series of connected stages:1. Automated Asset Discovery
The very first step in this automation process is to gain complete visibility into every asset within the organization. This encompasses:- On-premise servers and endpoints.
- Cloud resources like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- APIs and SaaS applications.
- Containers and Kubernetes clusters.
2. Continuous Vulnerability Scanning
Rather than sticking to quarterly or annual scans, automated solutions allow for continuous vulnerability scanning. This includes:- SAST (Static Application Security Testing) – Scanning source code for vulnerabilities.
- DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) – Testing applications while they’re running.
- SCA (Software Composition Analysis) – Identifying vulnerabilities in open-source dependencies.
- Container Security Scanning – Spotting misconfigurations and vulnerabilities within container images.
- Secret Scanning – Finding hardcoded credentials and API keys in repositories.
3. Correlation & Deduplication
When multiple scanners are in play, results can often overlap. Automating helps to eliminate duplicate findings, consolidate results, and provide a single source of truth for security teams. This way, time isn’t wasted on addressing the same vulnerability repeatedly.4. Risk-Based Prioritization
Automating vulnerability management isn’t just about the numbers; it’s about what matters most. Tools leverage contextual data such as:- CVSS Scores – A standardized severity rating.
- Exploit Intelligence – Whether the vulnerability is currently being exploited in the wild.
- Business Context – Whether the affected asset is crucial for key business functions.
5. Remediation Workflow Automation
Prioritized vulnerabilities are automatically pushed into remediation platforms. Some examples include:- Creating Jira or ServiceNow tickets.
- Sending Slack or Microsoft Teams alerts.
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines to prevent vulnerable code from being deployed.
6. Verification & Retesting
After remediation, automated retesting validates whether vulnerabilities have been successfully fixed or not. It closes the loop and eliminates repeat issues.Why Manual Vulnerability Management Is Inadequate?
Companies that use manual processes are hindered by the following:Volume and Scale
Thousands of results can be returned from a single vulnerability scan. Manually sorting and prioritizing them can be an exercise that lasts weeks, with critical vulnerabilities open in the meantime.Human Error
Manual triage commonly brings about inconsistencies. Various team members can have differing priorities for vulnerabilities, causing delays or overlooked risks.Lack of Continuous Monitoring
Periodic scans leave vulnerabilities undetected for months. Automated scanning, on the other hand, operates all the time and identifies exposures in real-time.Ineffective Remediation Processes
Vulnerabilities are followed in spreadsheets or stand-alone systems without automation. This slows down communication between IT and security teams, resulting in higher mean time to remediate (MTTR).Traditional Vulnerability Management Vs Automated Vulnerability Management
 In the image below, we provided a detailed comparison between traditional vulnerability management and automated vulnerability management. This analysis will clarify the key differences, emphasizing the advantages of automation in enhancing security practices.
In the image below, we provided a detailed comparison between traditional vulnerability management and automated vulnerability management. This analysis will clarify the key differences, emphasizing the advantages of automation in enhancing security practices.