March may have roared in like a lion, but for cybersecurity professionals, it was more like a backdoor sneaking into a critical utility. This month, we’ve seen some serious contenders, but one in particular has sent shockwaves through the open-source software (OSS) community: CVE-2024-3094, a sneaky supply chain attack targeting the widely used XZ Utils package. Let’s dive in and explore the top 5 vulnerabilities this month, with a special focus on this OSS nightmare.
1. CVE-2024-3094 – XZ Utils Supply Chain Attack Severity:
Critical This one’s a doozy, folks. Malicious code allowing unauthorized remote SSH access was discovered in XZ Utils, a package used by major Linux distributions. The attacker played the long game, building a credible reputation over years before striking. The payload modifies OpenSSH server decryption routines, allowing attackers to execute code before authentication. It’s a prime example of how trust in the OSS community can be exploited.
Here’s a more detailed explanation of CVE-2024-3094:
- Supply Chain Compromise: Attackers infiltrated the legitimate development process of XZ Utils to inject malicious code. This technique is particularly dangerous because it can be difficult to detect and can impact a wide range of systems that rely on the vulnerable software.
- Backdoor Installation: The malicious code created a backdoor that could be used by attackers to gain remote access to affected systems. This backdoor specifically targeted the SSH daemon, which is a program that allows secure remote login to Linux systems.
- Remote Code Execution (RCE): By exploiting the backdoor, attackers could potentially execute arbitrary code on vulnerable systems. This would give them complete control over the system and allow them to perform a variety of malicious activities.
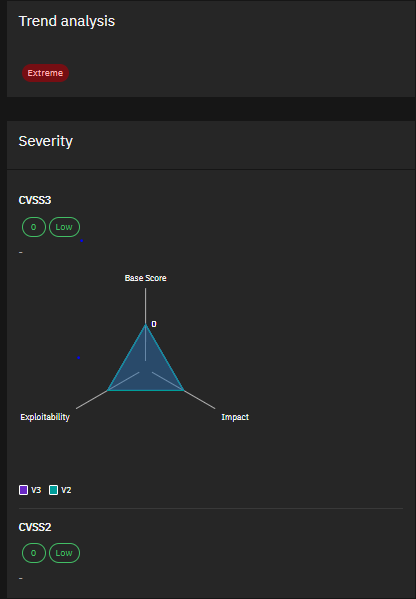
2. CVE-2024-1709 & CVE-2024-1708 – ConnectWise ScreenConnect Vulnerabilities Severity:
Critical Threat actors are actively exploiting these critical vulnerabilities in ConnectWise ScreenConnect servers. CVE-2024-1709 allows authentication bypass, while CVE-2024-1708 enables path traversal. Successful exploitation can lead to ransomware deployment and cryptocurrency mining. Patch your servers ASAP!
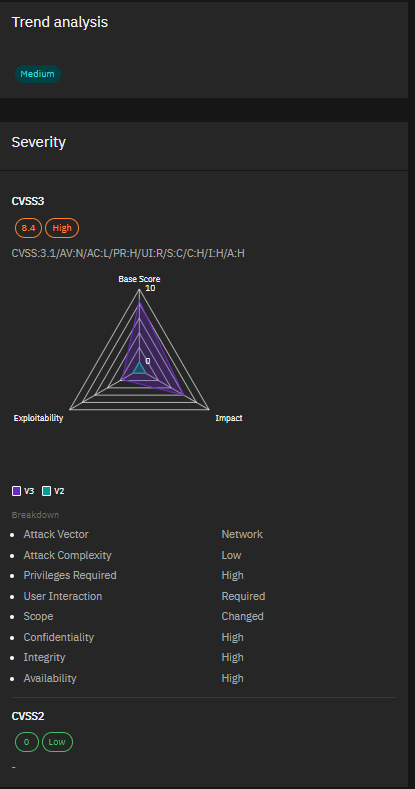
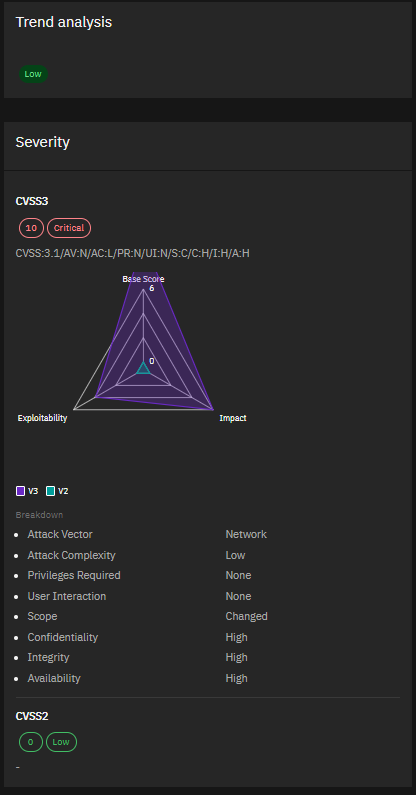
3. CVE-2024-21407 & CVE-2024-21408 – Windows Hyper-V Vulnerabilities Severity:
Critical Microsoft’s March Patch Tuesday addressed 60 flaws, including these two critical bugs in Windows Hyper-V. CVE-2024-21407 allows remote code execution, while CVE-2024-21408 can cause denial of service. With virtualization being a key component of many infrastructures, these vulnerabilities demand immediate attention.
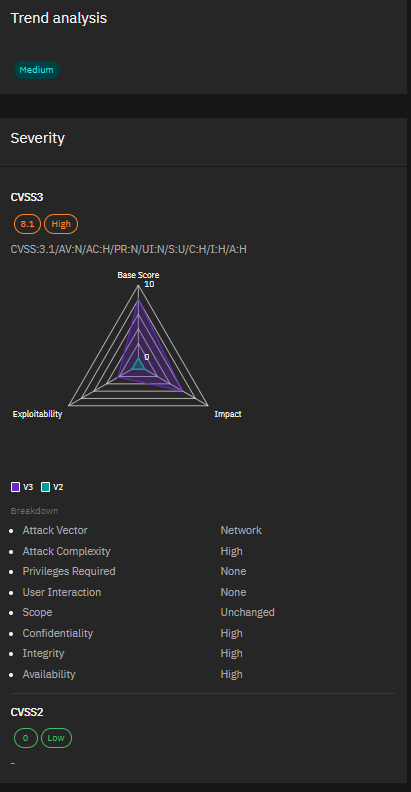
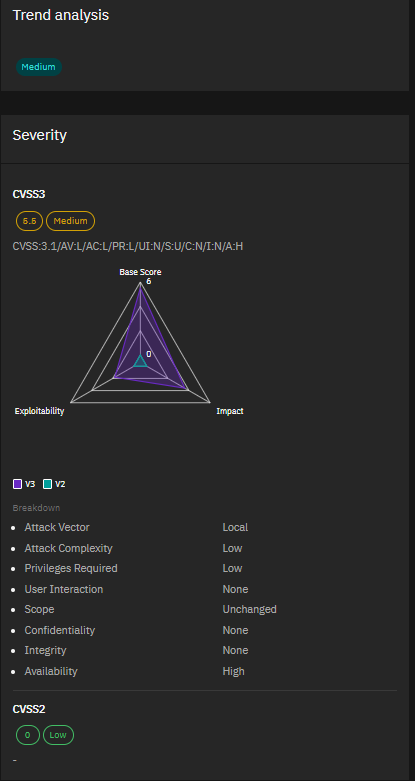
4. CVE-2023-42789, CVE-2023-42790 & CVE-2023-46717 – Fortinet FortiProxy and FortiOS Vulnerabilities Severity:
Critical to Medium Fortinet released patches for two critical and one medium severity vulnerabilities affecting FortiProxy and FortiOS. The critical flaws (CVE-2023-42789 and CVE-2023-42790) can allow arbitrary code execution, while the medium severity issue (CVE-2023-46717) enables privilege escalation. Stay on top of your Fortinet updates to mitigate these risks.
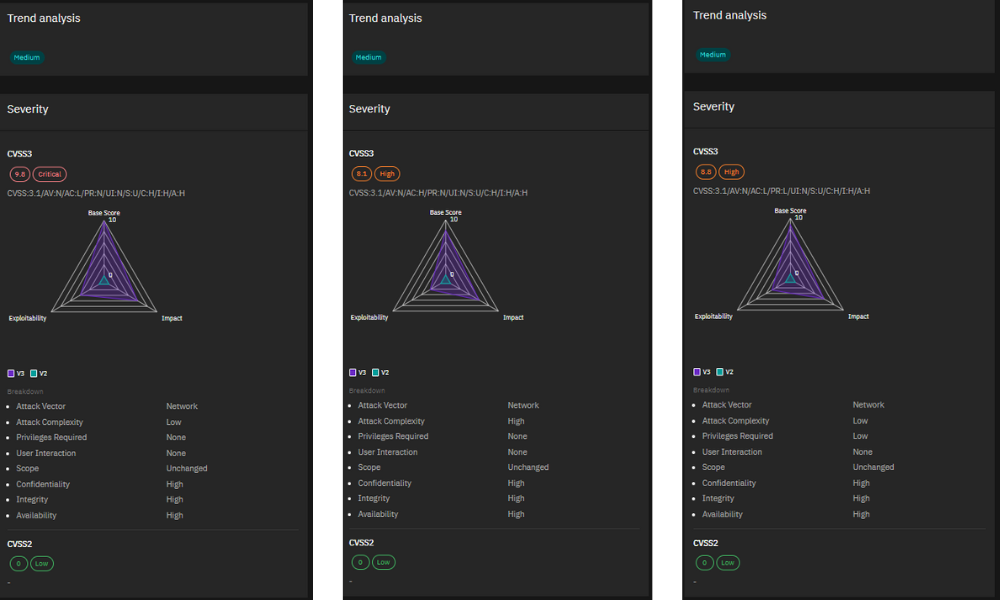
5. Multiple CVEs – Mozilla Firefox Vulnerabilities Severity:
Critical to Moderate Mozilla released fixes for a range of vulnerabilities in Firefox, addressing issues like arbitrary code execution, out-of-bounds memory read, memory corruption, timing side-channel attacks, and clickjacking. With exploits ranging from critical to moderate severity, it’s crucial to update your Firefox installations to the latest patched versions.
Now, let’s circle back to CVE-2024-3094, the XZ Utils supply chain attack. This incident highlights the importance of vigilance and security measures within the OSS community. It’s a stark reminder that even trusted projects can be compromised by determined attackers. As we always emphasize, layered security is key. Regularly update your software, monitor for suspicious activity, and have a solid incident response plan in place.
In the case of CVE-2024-3094, affected users should immediately downgrade XZ Utils to a safe version (5.4.6 or earlier) and restart their OpenSSH servers. If downgrading isn’t possible, you can use the backdoor’s “kill switch” by adding a specific string to your /etc/environment file.
The XZ Utils attack also underscores the need for thorough code reviews and continuous security testing in OSS projects. Tools like Google’s oss-fuzz can help catch potential vulnerabilities early on. It’s a collective responsibility to maintain the integrity of the OSS ecosystem.
To wrap up, March 2024 has been a wild ride in the world of cybersecurity. As always, stay informed, keep your systems updated, and don’t hesitate to reach out to the security community for help. Together, we can navigate these challenges and build a more secure future.
Until next time, stay safe out there!