Data breaches recorded a high-impact breach across apparel brands, analytics platforms, food-delivery networks, cloud providers, and major financial institutions. These incidents exposed sensitive customer data, internal records, and operational details, showing how easily exposure spreads when vendors, cloud setups, or internal controls fall short.
Under Armour, Mixpanel, DoorDash, Oracle, and leading Wall Street institutions all faced unauthorised data access during the month. These cases provide a clear view of how attackers continue to target high-value systems and how quickly exposure spreads when safeguards fail to catch early signs of intrusion.
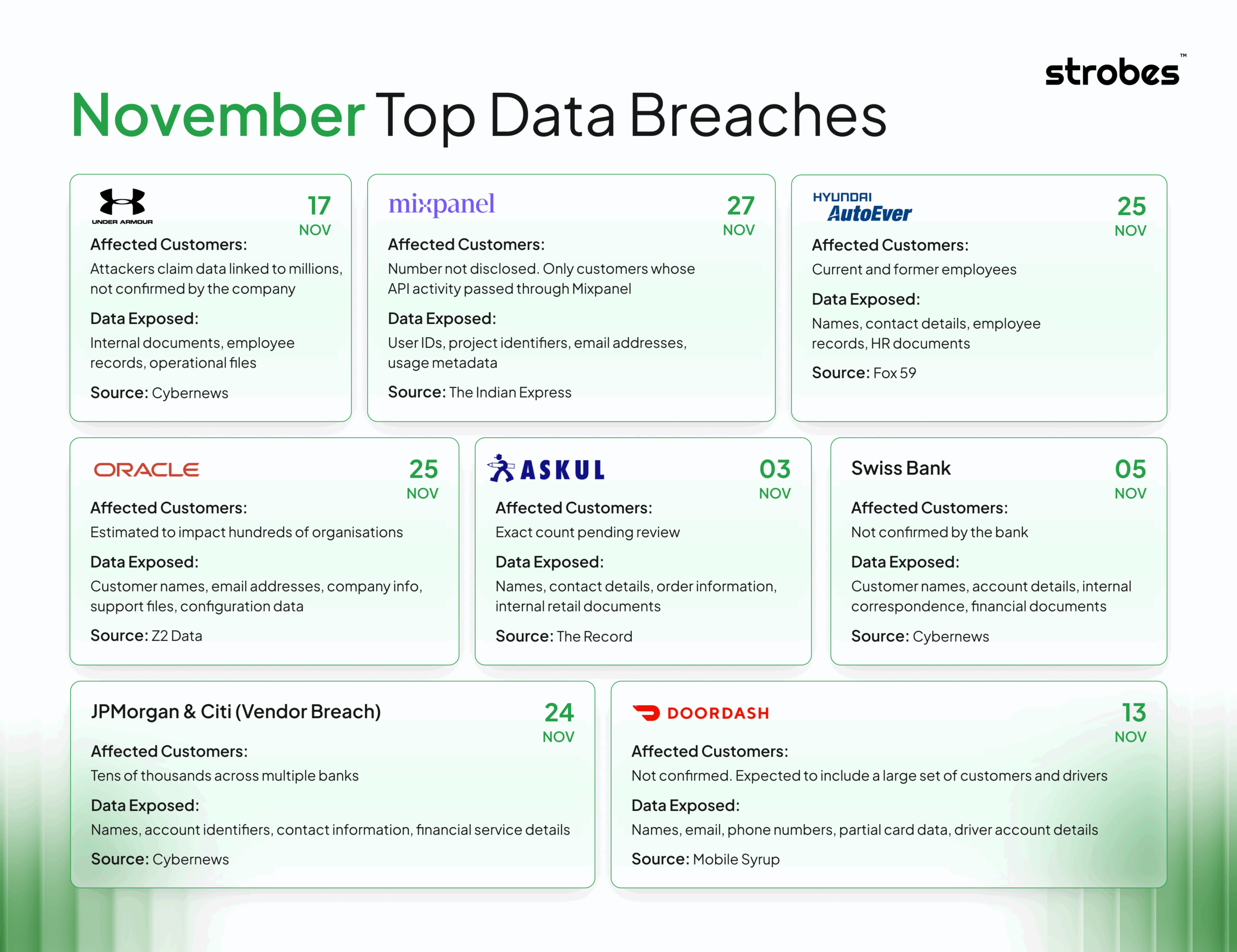
1. Under Armour Ransomware Incident Exposes Internal Data, Hackers Claim “Millions” Impacted
Incident Overview:
Under Armour faced a ransomware attack targeting internal corporate systems. The threat group behind the intrusion claimed they accessed and copied a large volume of data, including “millions of personal data” records. While the company has not confirmed the attacker’s claim, they acknowledged that certain files stored on internal servers were accessed without permission.
What Data Was Exposed:
Preliminary evidence suggests the attackers obtained internal documents, employee-related records, and operational files. Under Armour has not published a complete data inventory yet since the investigation is still active.
Number of Affected Individuals:
The ransomware group claims the breach involves data linked to millions of individuals. Under Armour has not validated this number, and the final count may shift as forensics continue.
Business Impact:
The attack caused interruptions across internal environments. It also increased compliance workload, exposed the company to legal scrutiny, and raised concerns across its global workforce and partners. Reputational risk remains high due to the claim of large-scale personal data exposure.
Company Response:
Under Armour isolated compromised systems, activated incident response teams, and notified relevant authorities. They engaged external forensics specialists to assess the extent of data access and began communication with potentially impacted stakeholders.
Key Lesson:
Ransomware actors now prioritise exfiltration over encryption. Companies with large data stores must strengthen monitoring, validate access anomalies faster, and maintain a ready-to-deploy incident workflow to reduce impact from such data-theft-first attacks.
Date of Breach: 17 November 2025
Source: Cybernews
2. Mixpanel Breach Exposes OpenAI API Customer Details and User IDs
Incident Overview:
OpenAI confirmed a data exposure incident after Mixpanel, its analytics provider, experienced unauthorised access. Attackers accessed event logs stored in Mixpanel’s environment, which contained certain OpenAI API customer metadata. The breach affected Mixpanel’s systems, not OpenAI’s core infrastructure.
What Data Was Exposed:
The exposed logs included user IDs, project identifiers, customer email addresses, and usage-related metadata. OpenAI verified that no API keys, passwords, payment information, model outputs, or fine-tuned data were included in the compromised dataset.
Number of Affected Individuals:
OpenAI has not disclosed the exact count. Based on available updates, only customers whose activity passed through Mixpanel during the affected logging period were impacted.
Business Impact:
The incident increased scrutiny on external analytics tools used by companies handling sensitive workloads. It forced OpenAI and Mixpanel to review log fields, remove unnecessary data collection, and address customer concerns about third-party data handling. Compliance work also increased across both organisations.
Company Response:
OpenAI immediately disabled the Mixpanel integration, notified impacted customers, and began auditing all external analytics pipelines. Mixpanel contained the breach, locked down compromised access, and engaged external forensics specialists. Both companies are validating the scope and reinforcing controls.
Key Lesson:
Analytics tools often collect more metadata than teams expect. Organisations should enforce strict field-level controls, minimise vendor data exposure, and review logging output regularly to prevent unintended information leakage.
Date of Breach: November 27, 2025
Source: The Indian Express
3. DoorDash Suffers Another Data Breach Through Third-Party Vendor Access
Incident Overview:
DoorDash confirmed a new data breach after attackers gained unauthorised access through a compromised third-party service provider. The intrusion exposed both customer and driver information managed by the vendor. This added to previous security incidents, raising concerns about recurring weak points in the company’s extended ecosystem.
What Data Was Exposed:
The exposed data included customer names, email addresses, phone numbers, and partial card information. For drivers, certain account-related details were also involved. DoorDash noted that full payment details, bank account numbers, and passwords were not part of the exposed dataset.
Number of Affected Individuals:
DoorDash did not publish a precise number. Early reports indicate that a significant portion of users and drivers connected to the vendor platform during the affected period were impacted.
Business Impact:
The breach increased the workload related to customer notifications, regulatory filings, and vendor system reviews. It also placed the brand under stronger public scrutiny since this incident followed previous breaches linked to partner systems.
Company Response:
DoorDash immediately cut off access to the compromised vendor, began an internal investigation, and alerted authorities. External cybersecurity experts were brought in to validate the extent of the exposure. Notifications to affected customers and drivers were also initiated.
Key Lesson:
Vendor-linked exposures remain a critical weak point for companies handling large volumes of user data. Stronger monitoring, strict data-sharing controls, and regular audits of third-party partners are necessary to avoid repeated incidents.
Date of Breach: November 13, 2025
Source: Mobile Syrup
4. Oracle Data Breach Exposes Customer Information Through Compromised Cloud Infrastructure
Incident Overview:
Oracle reported a data breach after attackers gained unauthorised access to a portion of its cloud environment. The intrusion was linked to misconfigured cloud resources that allowed external access to stored customer data. The incident affected a subset of Oracle’s cloud services used by enterprise clients.
What Data Was Exposed:
Based on early disclosures, the exposed dataset included customer names, email addresses, company information, support-related files, and internal configuration details stored in the affected cloud buckets. No passwords, financial data, or internal source code were part of the exposed assets.
Number of Affected Individuals:
Oracle did not release a specific number. Security researchers estimate that the breach impacted hundreds of organisations using Oracle’s cloud services during the affected period. The final count may only be known after each impacted customer completes its internal review.
Business Impact:
The breach created operational pressure across Oracle’s customer base, including compliance notifications, cloud environment reviews, and audits of how data was stored. It also led to closer inspection of cloud configuration practices and increased concern about shared-responsibility gaps within large cloud ecosystems.
Company Response:
Oracle secured the exposed cloud resources, worked with affected customers, and engaged external experts to confirm the scope. They issued updated configuration guidance, deployed additional monitoring controls, and notified regulators where required.
Key Lesson:
Misconfigured cloud storage continues to be one of the most common sources of enterprise data leaks. Strict configuration reviews, automated checks, and continuous monitoring are essential to prevent exposure of stored data.
Date of Breach: November 25, 2025
Source: Z2 Data
5. Customer Data from Wall Street Banks Exposed in Vendor Breach Affecting JPMorgan and Citi
Incident Overview:
A third-party service provider used by multiple Wall Street institutions reported a breach that exposed customer information linked to JPMorgan, Citi, and other financial firms. Attackers gained access to the vendor’s environment and extracted files containing sensitive client records handled on behalf of these banks.
What Data Was Exposed:
The exposed dataset included customer names, account-related identifiers, contact information, and certain financial service details processed by the vendor. No full bank account numbers, passwords, or transaction authorisation data were part of the leaked files.
Number of Affected Individuals:
The exact number has not been formally disclosed. Early reporting suggests that tens of thousands of customers across several financial institutions may be affected, but final confirmation will depend on ongoing audits.
Business Impact:
The breach created operational pressure for all impacted banks. It triggered regulatory filings, customer notifications, and internal reviews of third-party data practices. The event also raised concerns about vendor oversight within the financial sector, where strict controls are expected.
Company Response:
JPMorgan, Citi, and other affected institutions worked with the vendor to contain the breach and secure the compromised systems. They launched their own investigations, notified impacted customers, and began coordinating with regulators. Additional checks on vendor access and data-handling standards were initiated.
Key Lesson:
Financial institutions often rely on vendor ecosystems to manage high-volume customer operations. When these vendors are not monitored closely or lack strong controls, exposure risks can escalate across multiple banks at once.
Date of Breach: November 24, 2025
Source: Cybernews
6. Swiss Bank Hit by Cyberattack, Hackers Claim to Have Stolen Customer Data
Incident Overview:
Swiss bank reported a cyberattack after a threat group claimed to have accessed and stolen sensitive customer information. The attackers stated they extracted internal files linked to client operations and financial records. The bank confirmed that certain systems were compromised, although the full scope of the intrusion is still under review.
What Data Was Exposed:
Based on early statements from the attackers, the stolen dataset includes customer names, account-related details, internal correspondence, and selected financial documents. The bank has not yet published a complete list of affected data categories as the investigation is ongoing.
Number of Affected Individuals:
The threat group claims the breach involves data from thousands of customers. The bank has not validated this figure, and the final count will be determined once forensic specialists complete their review.
Business Impact:
The incident created operational pressure across the bank’s internal teams, especially in compliance and customer support. The claim of financial document theft increases the risk of fraud attempts and regulatory scrutiny. The bank now faces reputational concerns due to the sensitive nature of the exposed information.
Company Response:
The bank isolated affected systems, engaged external cybersecurity firms, and notified relevant authorities. They also initiated direct outreach to impacted customers and began strengthening controls across internal systems and third-party connections.
Key Lesson:
Financial institutions remain prime targets due to the value of customer and transactional data. Strong access controls, regular audits, and continuous monitoring are essential to detect unauthorised data access before attackers extract sensitive information.
Date of Breach: November 5, 2025
Source: cybernews
7. Askul Confirms Data Leak After Cyberattack Linked to Russia-Based Group
Incident Overview:
Japanese retailer Askul announced a data leak after a Russia-linked threat group claimed responsibility for a cyberattack on its systems. The attackers said they accessed internal servers and extracted files that included customer and operational information. Askul confirmed unauthorised access and is still validating the full scope.
What Data Was Exposed:
Early findings indicate the exposed files contained customer names, contact details, order information, and internal documents connected to retail operations. Askul stated that payment card data was not part of the leaked dataset, but some personal details were taken.
Number of Affected Individuals:
Askul has not disclosed a final number. Initial reports suggest that the exposure may include data from thousands of customers, with the exact count to be confirmed after the forensic review.
Business Impact:
The breach disrupted internal processes, triggered compliance notifications, and raised concerns among customers due to the attackers’ public claims. The incident also added pressure on Askul’s IT and security teams, who now need to assess potential fraud risks linked to the leaked personal details.
Company Response:
Askul isolated affected systems, activated incident response teams, and began working with external cybersecurity specialists. They notified relevant authorities and started communicating with impacted customers. Additional controls and system reviews were introduced to prevent further exposure.
Key Lesson:
Retailers handling high-volume customer data are frequent targets for organised groups. Strong access controls, timely monitoring, and consistent review of internal systems help reduce exposure when attackers attempt to extract operational or customer-related information.
Date of Breach: November 3, 2025
Source: The Record
8. Hyundai AutoEver America Data Breach Prompts Investigation by Levi & Korsinsky, LLP
Incident Overview:
Hyundai AutoEver America, the IT services arm supporting Hyundai and Kia operations in the U.S., reported a data breach after discovering unauthorised access to systems containing employee and corporate information. Following the disclosure, law firm Levi & Korsinsky, LLP launched an investigation into the incident to determine the scope of exposure and potential legal obligations toward affected individuals.
What Data Was Exposed:
Based on early filings, the exposed information may include names, contact details, employee records, and certain HR-related documents. Hyundai AutoEver stated that financial information and customer vehicle data were not part of the compromised dataset, but some sensitive personal records tied to staff were accessed.
Number of Affected Individuals:
The company has not released an exact count. Initial reporting suggests that several thousand current and former employees may be impacted, with the final number pending the results of the internal and legal investigations.
Business Impact:
The breach created operational pressure across HR, IT, and legal teams. It also triggered regulatory reporting requirements and increased scrutiny because of the involvement of a major law firm. Employee trust and internal communication workloads have increased as the organisation works to assess potential misuse of the exposed data.
Company Response:
Hyundai AutoEver secured the affected systems, engaged external cybersecurity professionals, and notified employees about the incident. They also began cooperating with regulators and legal teams to confirm the full extent of exposure. Support services, including identity protection, were offered to individuals believed to be affected.
Key Lesson:
Organisations handling employee data should apply the same security standards they use for customer information. Strong access controls, regular system reviews, and incident-ready monitoring help reduce the impact when intrusions target HR or internal records.
Date of Breach: November 25, 2025
Source: Fox 59
Conclusion:
The breaches from November 2025 reinforce a clear pattern. Attackers take advantage of weak vendor practices, cloud misconfigurations, and unchecked data flows long before organisations detect the issue. Delays in monitoring or review give intruders more time to extract sensitive information and disrupt operations.
To avoid similar outcomes, organisations need consistent oversight across vendors, cloud assets, and internal systems. Continuous exposure discovery, faster validation paths, and stronger prioritisation help reduce these risks before they escalate. Strobes Security equips teams with the capabilities to identify, assess, and remediate exposures with clarity and speed. Strengthen your exposure management approach today. Book a demo with Strobes to see how Strobes can support your security operations.